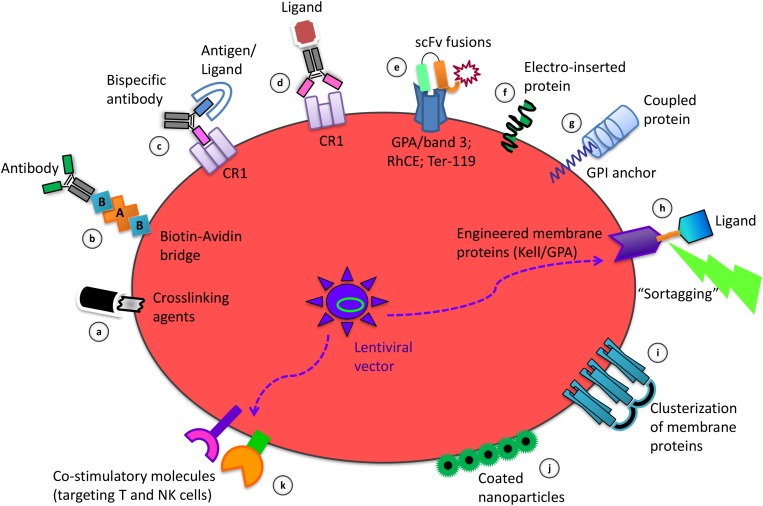
FIGURE 1.
Strategies of RBC membrane processing to obtain the delivery and targeting of therapeutic agents and to induce immune tolerance or immunogenicity. Among the coupling modalities for binding of molecules to the RBC surface there are: the use of crosslinking agents for chemical coupling of ligands (a); the biotinylation to couple selected antibodies by an avidin bridge (b); the use of bispecific antibodies targeting antigens/ligands to the RBC specific protein target CR1 (c); the crosslinking of antibodies carrying a specific ligand to Complement Receptor 1 (CR1) (d); the use of scFv-based fusion constructs targeting GPA/band 3, RhCE, Ter-119, on the RBC surface (e); the electro-insertion of transmembrane proteins into the RBC membrane (f); the coupling of proteins using the GPI lipid anchor (g); the Sortase A-mediated tagging (“sortagging”) of molecules to genetically engineered membrane proteins, expressed upon ex vivo transfection of erythroid precursors with lentiviral vectors, followed by their differentiation into enucleated RBC (h); the clusterization of RBC membrane proteins for selective targeting (i); the non-covalent attachment of coated nanoparticles to the RBC surface (j); the lentivirus-driven co-expression of combinations of co-stimulatory molecules on engineered RBC (k).