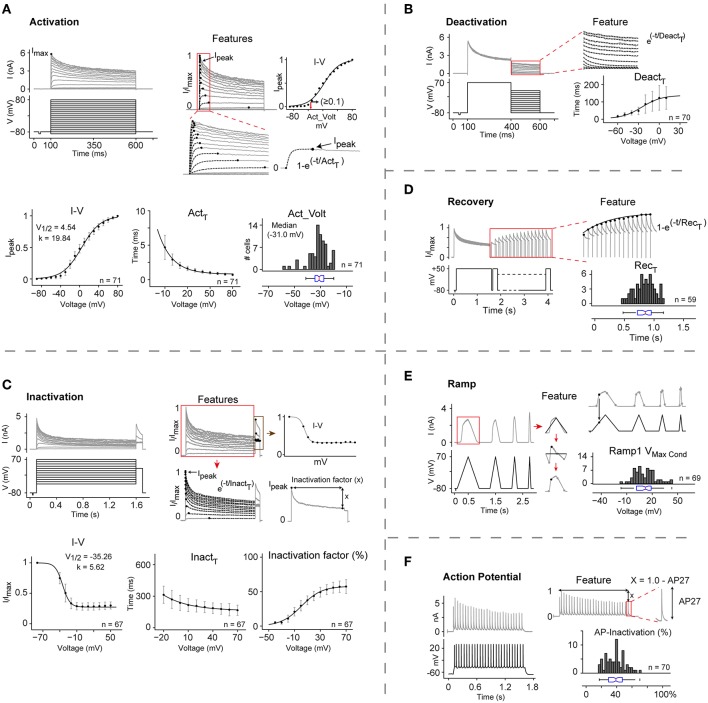
Figure 2.
Automated kinetic characterization of CHO rKv1.1 at 25°C. (A–F) The kinetic properties of rat Kv1.1 channel in CHO cells are extracted from the current response of six different voltage protocols: Activation, Deactivation, Inactivation, Inactivation recovery, and two in vivo-like stimuli, Ramp, and Action potential. Each panel shows the applied voltage stimulus (black traces), representative traces of the current responses (gray traces), region of interest for analysis (red box), and extracted features. For all analysis, current traces are first normalized to overall maximum current (Imax). All data are presented as means ± S.D. (A) I-V curve, activation voltage (Act_Volt), and activation time constant (Actτ) are extracted for all cells (n = 71). Peak current (Ipeak) for each trace is identified and plotted against command voltage to get I-V curve (top right panel). For each cell the voltage where normalized current (Ipeak) exceeds 0.1 in I-V curve is considered as the activation voltage (red arrow). Actτ is calculated by fitting single exponential curve from 0 to Ipeak for each current trace. Ipeak and Actτ from each cell are plotted and fitted with Boltzmann and single exponential function, respectively to get mean I-V curve and mean Actτ. (B) Deactivation time constant (Deactτ) for each trace is calculated by fitting a single exponential to current response during the second stimulus pulse (400–600 ms) and then plotted against command voltage (n = 70). (C) Inactivation curve, time constant (Inactτ), and inactivation factor are features extracted for all cells (n = 67). Ipeak from the second stimulus pulse (red box) are plotted against command voltage to get Inactivation curve. Inactτ is calculated by fitting a single exponential to each current trace from Ipeak to the end of the first stimulus pulse. Inactivation factor (x) is the difference from Ipeak to the end of the first stimulus pulse. Inactivation I-V, Inactτ, and Inactivation factors from all cells are averaged and plotted against command voltage and fitted with Boltzmann, single exponential, and Boltzmann function, respectively. (D) Inactivation recovery time constant (Recτ) is obtained by fitting a single exponential function to the peak current values of the responses to recovery pulses (red box) (n = 59). (E) Maximum conductance (Vmax_Cond) is calculated on the rising phase of the first Ramp (n = 69). (F) AP-Inactivation is measured by subtracting last AP (AP27) amplitude from normalized maximum value (1) (n = 70). Act_Volt, Recτ, Vmax_Cond, and AP-inactivation values for cell population are reported with histograms and box plots.