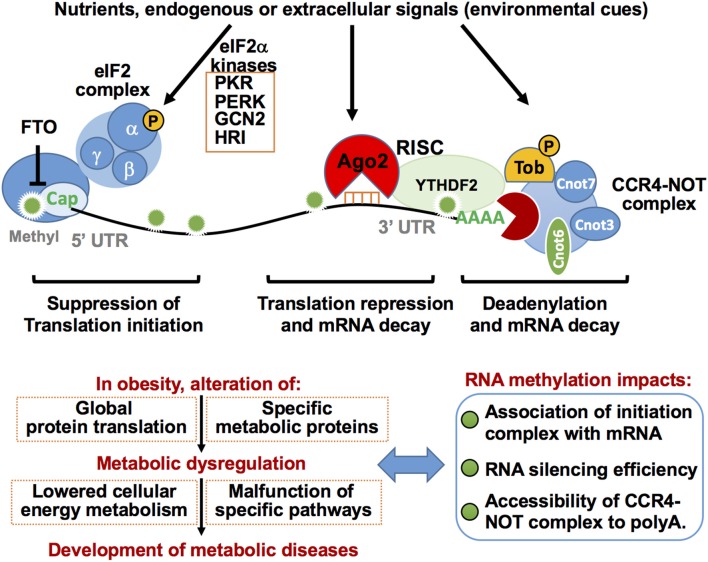
Figure 6.
Post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA translation repression eIF2a complex, Ago2-mediated RNA silencing, and decay and deadenylation via CCR4-NOT complex in metabolic regulation. RNA stability is increased by m7Gppp cap-adjacent m6Am. The m7Gppp cap is recognized by the protein initiation complex for protein translation. Conversely, eIF2a phosphorylation induced by eIF2a kinases in response to a variety of environmental cues results in inhibition of protein translation. Removal of the m7Gppp cap by the decapping enzyme DCP2 is a key step in mRNA decay. Ago2-mediated RNA silencing represses mRNA translation and induces its decay. The CCR4-NOT protein complex binds and deadenylates the poly(A) tail of target mRNA to stimulate mRNA decay. Ago2 RNA silencing machinery interacts with CCR4-NOT complex resulting in rapid mRNA decay and/or translation repression. TOB protein recruits CCR4-NOT deadenylase to a specific mRNA poly(A) tail by direct binding to Cnot7. Functions of these components are highly integrated into cellular metabolic homeostasis, at least in part, by regulating the efficiency of global protein translation and/or expression of specific metabolic proteins. Altered RNA methylation patterns on mRNA induced in obesity may affect these processes and thereby disrupt cellular metabolic homeostasis.