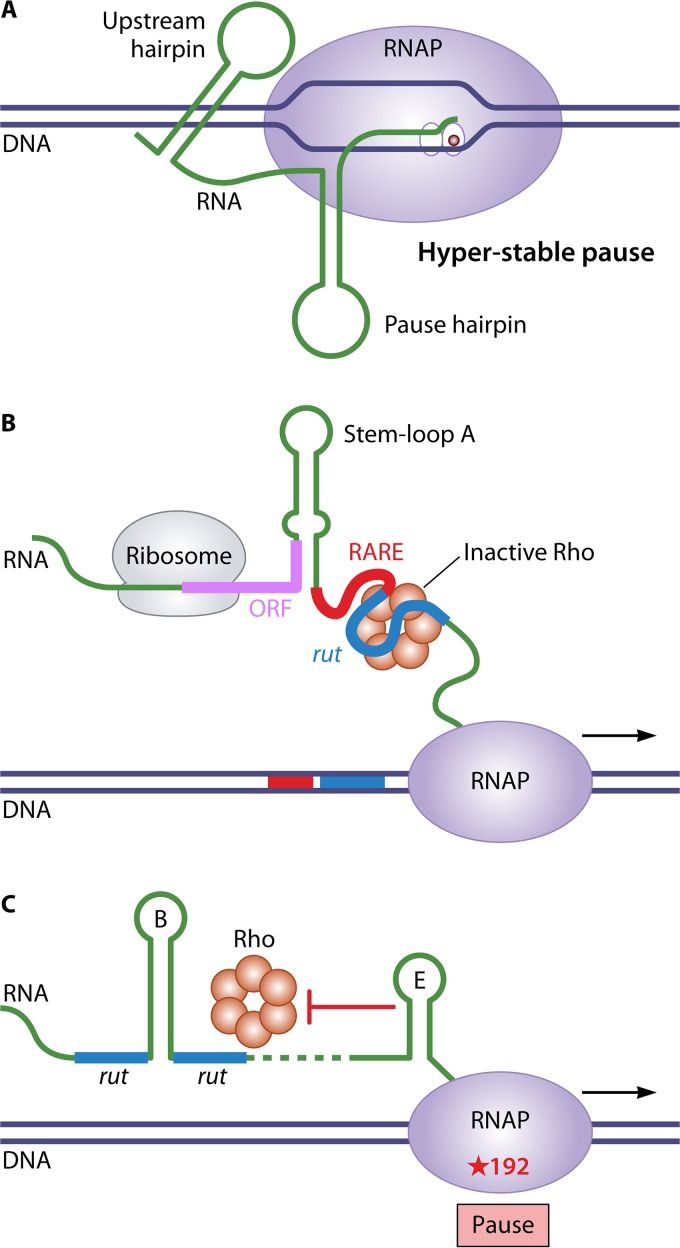
FIG 11.
Examples of non-rut site targets for regulating Rho-dependent attenuation. (A) Prolonged transcription pausing in the mgtA leader region. Under conditions of high Mg2+ levels, an upstream secondary structure in the leader transcript interacts with RNAP stalled at a hairpin-stabilized pause site to promote unique hyperstable transcription pausing. (B) RARE-mediated inactivation of Rho in the mgtCBR leader region. Under conditions of low Mg2+ levels, translation of a short leader ORF is inefficient, which promotes formation of a transcript secondary structure that exposes a single-stranded RARE immediately upstream of a rut site. When Rho binds the rut site, a single-stranded RARE can trap Rho in an inactive state, thereby permitting transcription through the mgtBCR structural genes. (C) Controlling the location of transcription termination in the corA leader region. Rho can bind the leader transcript at a discontinuous rut site interrupted by stem-loop B and translocate toward RNAP paused at position 192. However, stem-loop E prevents Rho from accessing RNAP at this site, thus promoting downstream Rho-mediated termination, typically at a pause site at position 240.