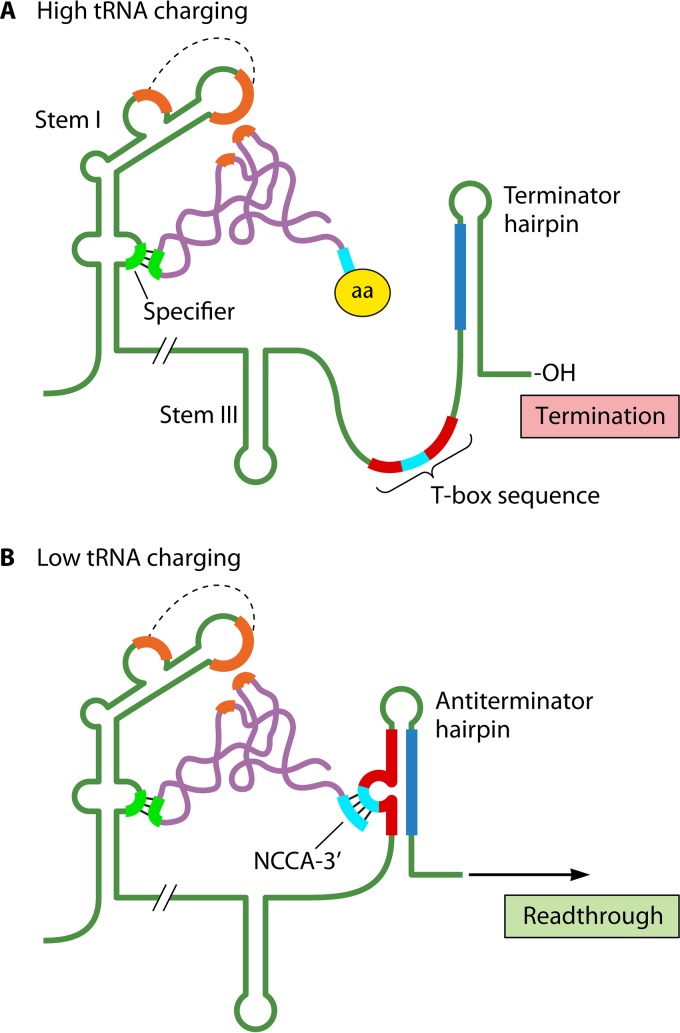
FIG 6.
T-box mechanism. (A) High-tRNA charging. The anticodon (chartreuse) of a charged cognate tRNA (purple) base pairs with the specifier sequence (chartreuse) in stem I of the leader RNA. The amino acid (aa) at the 3′ end of the tRNA prevents its interaction with the T-box sequence (red with central 7 bases in cyan), resulting in terminator hairpin formation and transcription termination within the leader region. (B) Low-tRNA charging. The anticodon of an uncharged cognate tRNA base pairs with the specifier sequence as described above, and the sequence NCCA at the 3′ end of the tRNA (cyan) hybridizes to a complementary sequence (cyan) within the central 7 bases of the T-box sequence. The latter interaction stabilizes formation of the antiterminator hairpin, which precludes terminator hairpin formation and allows transcription into the structural gene(s). Also shown in both panels is a recently discovered stacking interaction (orange) between the elbow of the cognate tRNA and the stem I platform. The dashed lines indicate interacting sequence motifs. For clarity, stem II in the leader transcript was omitted in both panels.