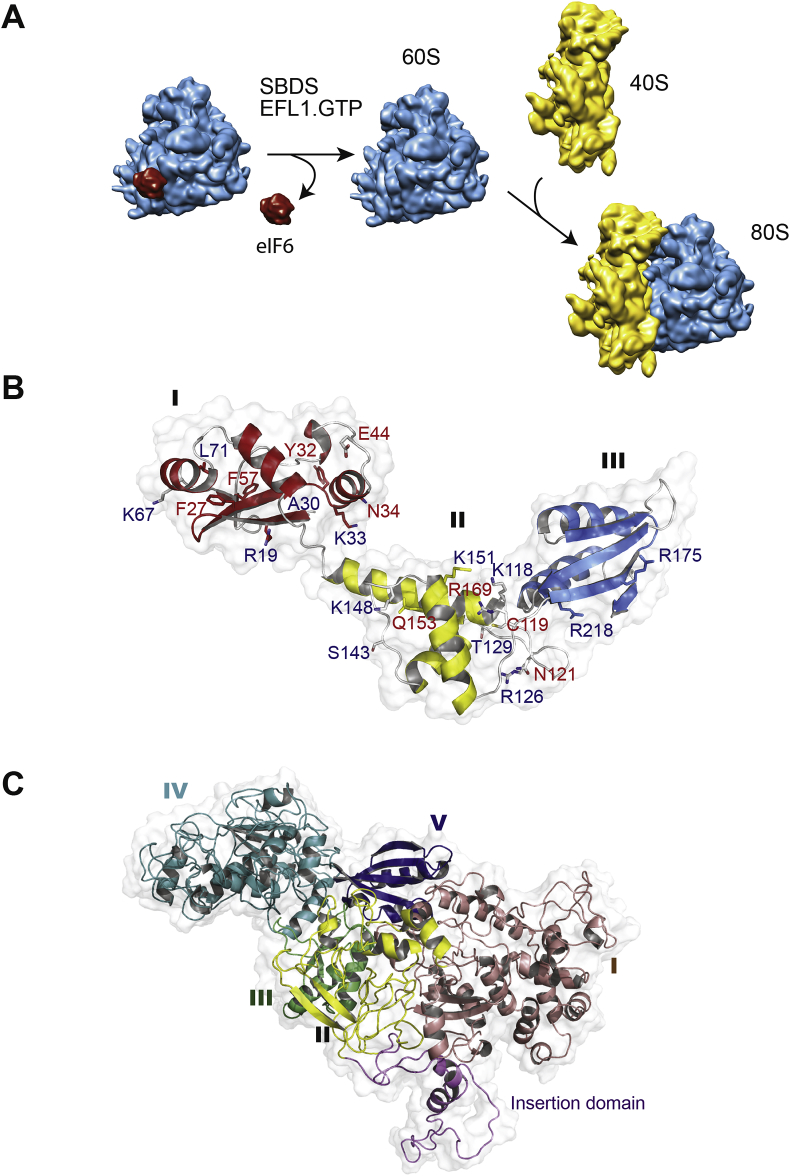
Fig. 2.
SBDS and the EFL1 GTPase cooperate to catalyse eIF6 eviction.
(A) Schematic showing that SBDS cooperates with the GTPase EFL1 in the cytoplasm to catalyse release of the anti-association factor eIF6 from the 60S subunit joining face to allow subunit joining and the formation of translation-competent 80S ribosomes. 40S subunit is coloured yellow, 60S subunit is cyan, eIF6 is red. (B) Ribbon representation of the human SBDS NMR structure. Domain I is coloured red, domain II is yellow, domain III is blue and loops are coloured grey. SDS-associated mutations modify surface epitopes (red text) or affect protein stability (blue text).
(C) Ribbon representation of the atomic model of human EFL1 (Weis et al., 2015), with domain I coloured violet, domain II yellow, domain III green, domain IV cyan and domain V blue.