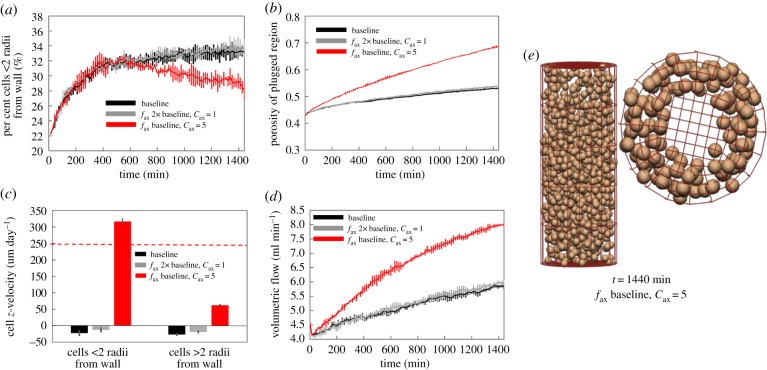
Figure 6.
When increasing the axial chemotaxis force alone (fax at 2× baseline, cax = 1), the plug generally stays intact, but moves as a whole either with or against the flow. By localizing the axial chemotaxis force at the wall (fax at 2× baseline, cax = 5), the model can predict physiological migration rates near the wall, and much lower migration rates for cells in the plug. However, plug break-up occurs more rapidly. (a) The percentage of cells within two cell radii of the vessel wall, (b) changes in plug porosity over time, (c) average z-velocity of cells (horizontal dashed line shows expected migration rate along the vessel wall) and (d) increases in predicted blood flow within the artery for a fixed pressure drop. (e) When axial chemotaxis is restricted to near the vessel wall, cells migrate primarily along the vessel wall. (Online version in colour.)