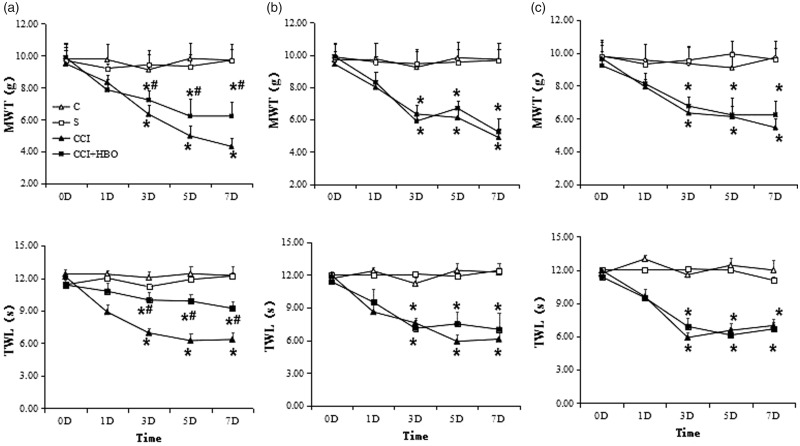
Figure 3.
MWT and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) in each group (n = 9 rats per group). In (a), we could see the value of MWT and TWL decreased on third, fifth, and seventh day gradually after CCI in normal group which decreased most in CCI group than those in CCI+HBO group (n = 9 rats per group for three repeats, *presented compared with S group, P < 0.05). And the value of MWT and TWL in the CCI+HBO group was higher than that in CCI group (# presented compared with CCI group, P < 0.05). After CC administration, the value of MWT and TWL also decreased on third, fifth, and seventh day after CCI in (b) (n = 9 rats per group for three repeats, *presented compared with S group, P < 0.05). However, the difference of MWT and TWL in CCI group and in CCI+HBO group is smaller than before (n = 9 rats per group for three repeats, P > 0.05). The similar phenomenon happened after STO609 administration. The value of MWT and TWL also decreased on third, fifth, and seventh day after CCI in (c) (n = 9 rats per group for three repeats, *presented compared with S group, P < 0.05). However, the difference of MWT and TWL in CCI group and in CCI+HBO group was not significant (n = 9 rats per group for three repeats, P > 0.05). MWT: mechanical withdrawal threshold; TWL: thermal withdrawal latency.