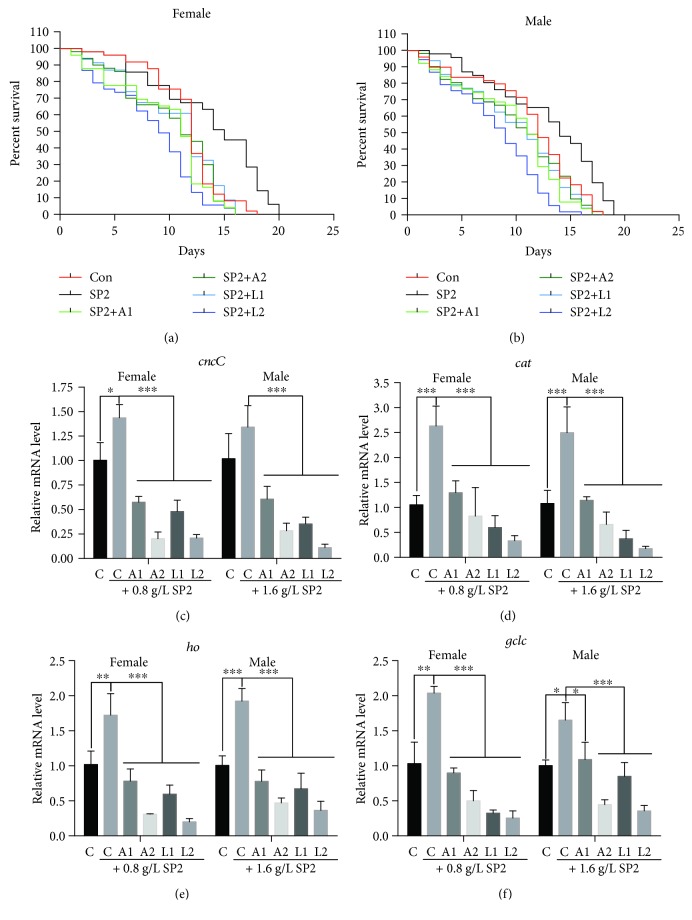
Figure 6.
SP2-mediated stress-resistant effect in fruit flies is dependent on the CncC/Nrf2/ARE signaling. Fruit flies were reared on medium containing no SP2 (Con) or different concentrations of SP2 (0.4 g/L (LSP), 0.8 g/L (MSP), and 1.6 g/L (HSP)) without and with all-trans-retinoic-acid (A1, 0.125 g/L; A2, 0.25 g/L) or luteolin (L1, 15 μmol/L; L2, 30 μmol/L), and the survival rates of the flies were determined. (a) Survival rate of male flies; (b) survival rate of female flies. In addition, samples of the flies were also taken after 10 days of treatment, and the transcript levels of cncC (c), cat (d), ho (e), and gclc (f) were then measured by qRT-PCR using the rp49 gene as a reference gene. The expression levels of the genes were evaluated by the ΔΔCt method, and then normalized to those of the corresponding control. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three determinations, each used the RNA extracted from 15 flies. “∗,” “∗∗,” and “∗∗∗” indicate a significant difference at the P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001 levels, respectively.