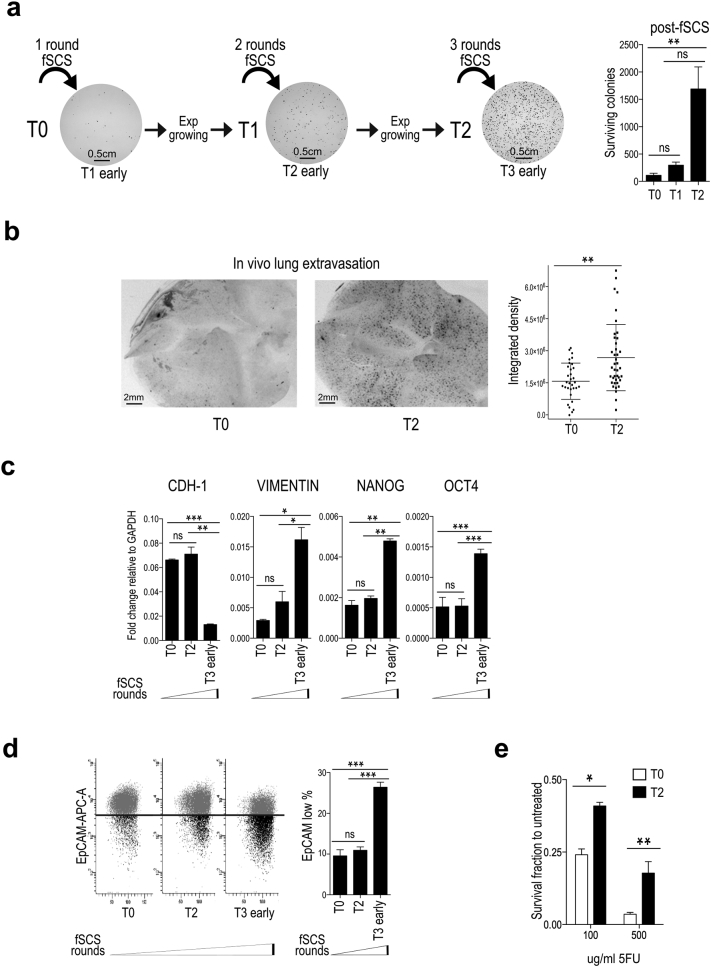
Fig. 2.
Multiple rounds of forced single cell suspension assay (fSCS) enrich for cells showing increased resistance to fSCS, in vivo extravasation ability and chemo-resistance. (a) Left: scheme of the experimental procedure to obtain fSCS-resistant cells and representative images of surviving colonies. Right: bars in graph represent mean +/− std. of the number of colonies generated by T0, T1 and T2 cells after fSCS (ns, non-significant; **p < .005, using paired t-test assuming unequal variances). (b) In vivo extravasation assay. Left: representative stereomicroscope images (1.5× magnification) of nude mice whole lungs at 72 h after intravenous injection of DiI labeled T0 and T2 cells, (black spots = DiI positive infiltrated cells). Right: dot Plot indicates mean +/− std. of the signal from DiI stained infiltrated cells per field in lungs of 5 mice per condition, quantified as described in Materials and Methods (**p < .005, using non-parametric Mann-Whitney test). (c) qRT-analysis of CDH1, VIMENTIN, NANOG, OCT4 expression in HCT116 cells subjected to multiple rounds of fSCS. Bars indicate mean +/− sem of two independent biological replicates (ns, non-significant; *p < .05, **p < .005; ***p < .0005, using paired t-test assuming equal variances). (d) Analysis of EpCAM cell surface expression by FACS in HCT116 cells subjected to multiple rounds of fSCS; left: representative scatter plot images; right: graph with bars indicating mean +/− sem of the fraction of EpCAM low population from three independent biological replicates (ns, non-significant; ***p < .0005 using paired t-test assuming equal variances). (e) Cell viability of HCT116 T0 and T2 after 16 h treatment with the indicated doses of 5-Fluorouracil (5FU) assessed by MTT 48 h after treatment stopped. Bars represent the mean +/− std. of two independent experiments (*p < .05; **p < .005, using paired t-test assuming unequal variances).