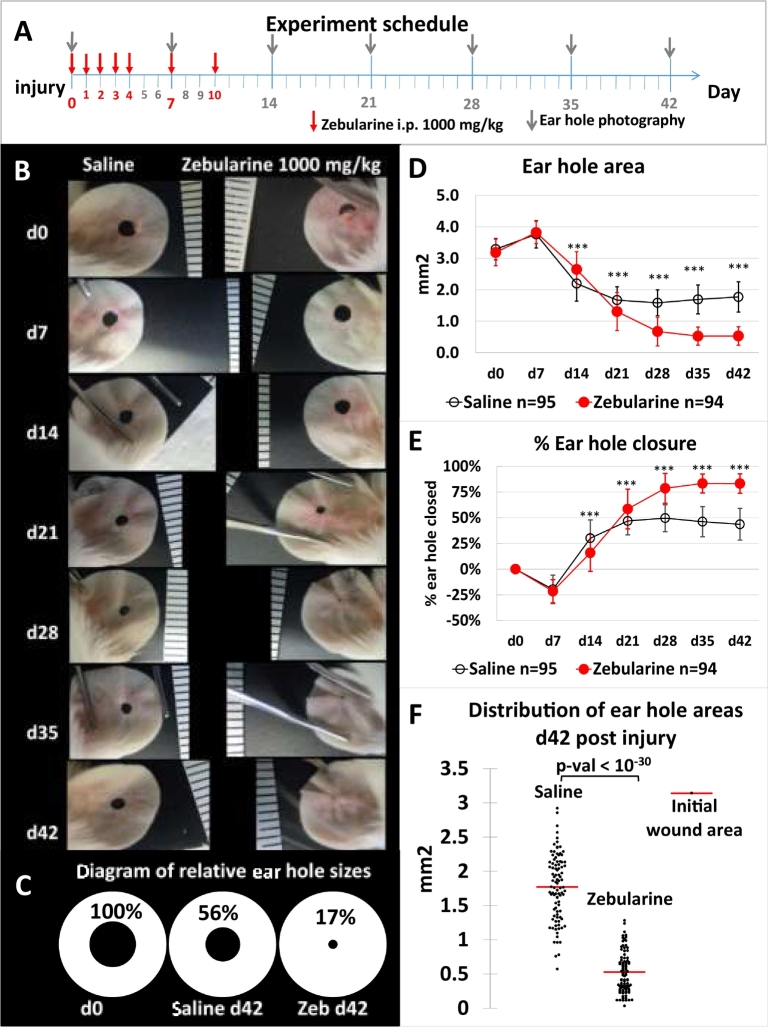
Fig. 1.
Zebularine stimulates ear pinna hole closure in the mouse. (A) Experimental time schedule. (B) Representative photographs showing ear hole closure for the same zebularine-treated and control female mice; the scale is calibrated in mm. (C) Diagram showing the mean ear hole area at day 0 (d0) and day 42 (d42) for zebularine-treated and control female mice. (D) Ear wound closure demonstrated as the mean hole area for 47 zebularine-treated and 48 control female mice; “n” indicates the number of ears, and the error bars represent the SD. (E) Mean percentage of closed area throughout wound healing; “n” indicates the number of ears, and the error bars represent the SD. (F) Distribution of ear hole areas at d42 post injury; each dot represents a single ear. The calculated p-values were as follows d14–2.42E-07, d21–3.01E-06, d28–0.00E+00, d35–0.00E+00, d42.