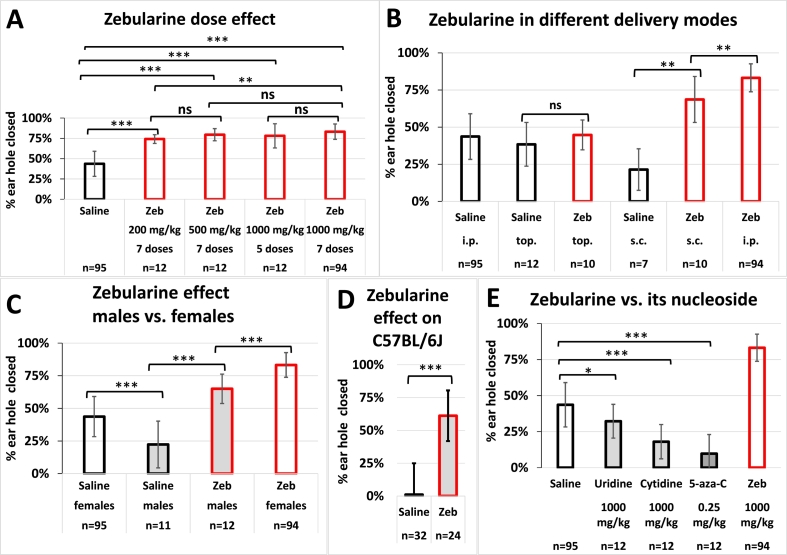
Fig. 2.
Zebularine, unlike its nucleotide analogues, promotes ear hole closure in mice at different doses and delivery modes and of different sexes and strains.(A) Similar effects of lower zebularine doses (200 and 500 vs. 1000 mg/kg) and shortened treatment periods (5 vs. 7 doses). (B) Results of topical, subcutaneous and intraperitoneal zebularine delivery (C) Zebularine effects in male and female mice. (D) Effective zebularine treatment in C57BL/6 J mice. (E) Effects of zebularine nucleoside analogues. Histograms show the mean ear hole area on day 42 post injury. Error bars represent the SD. If not indicated otherwise, the experiments were performed in BALB/c female mice that received 7 intraperitoneal injections of zebularine according to the time schedule presented in Fig. 1a. “n” refers to the number of ears from n/2 animals.