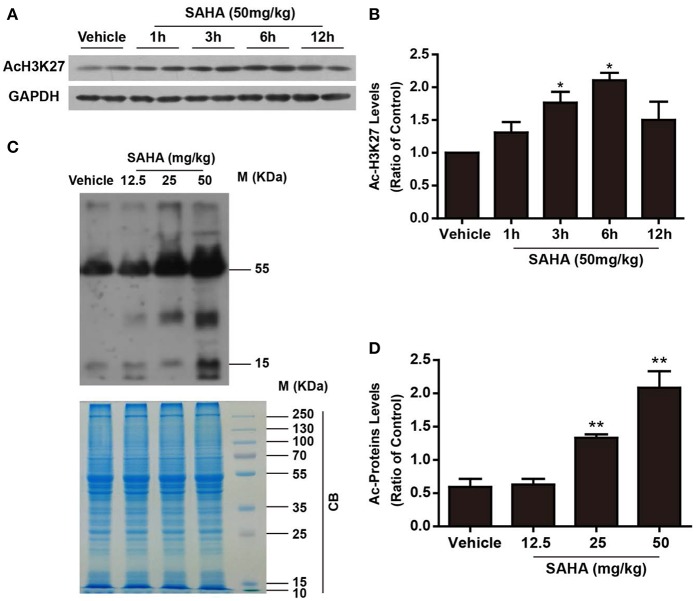
Figure 2.
The time- and dose-dependent effects of SAHA on protein acetylation levels in normal mouse brain. (A) The time-dependent effects of SAHA on histone acetylation. Normal mice received a single dose of SAHA (50 mg/kg, i.p.) and were sacrificed 1, 3, 6, and 12 h after injection. Proteins separated via SDS-PAGE were detected using an antibody against acetylated lysine (K) 27 of histone H3 (AcH3K27). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Densitometry analysis of acetylated H3K27, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with vehicle control. (C) The dose-dependent effects of SAHA on global lysine acetylation of brain proteins. Normal mice treated with 12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg SAHA were sacrificed at 6 h, and proteins extracted from brains were separated via SDS-PAGE and detected using an antibody against acetyl-lysine. Coomassie brilliant blue (CB) staining was used as a loading control. (D) Densitometry analysis of global lysine acetylation levels of mouse brain proteins. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 compared with vehicle control, n = 6/group.