Figure 1.
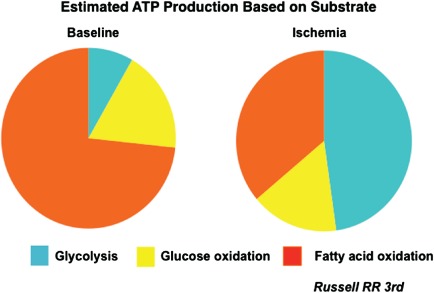
A diagrammatic representation of the relative proportion of myocardial substrate utilization. Under resting conditions, fatty acid metabolism contributes to nearly 70% to 75% energy generation, whereas the remaining comes from glucose metabolism (approximately 8% from glycolysis and 18% from oxidative metabolism). Myocardial substrate utilization changes dramatically with the onset of myocardial ischemia, with glycolysis contributing to nearly 50% of the energy production and a significant reduction in fatty acid uptake and metabolism. Courtesy of Dr. Raymond R. Russell, III, Yale University School of Medicine. Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate.
