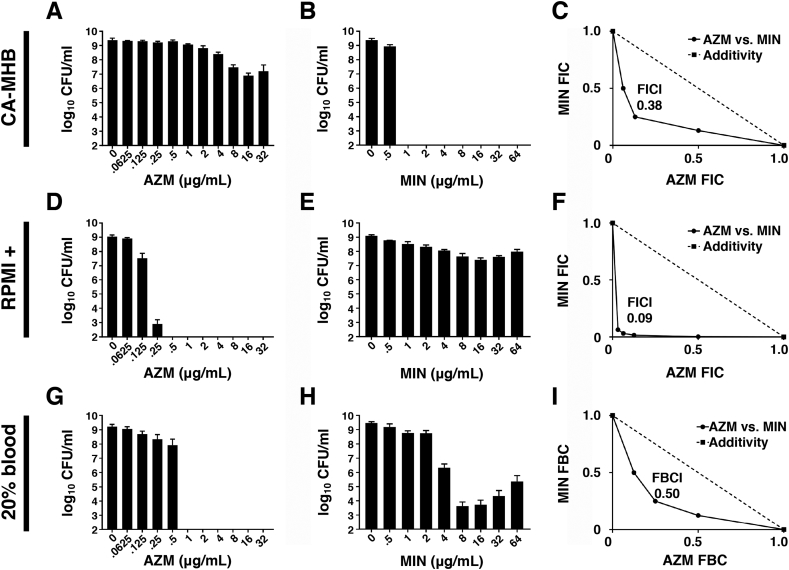
Fig. 1.
AZM and MIN show reciprocal media-dependent inhibitory activities vs. MDR A baumannii and synergize strongly when combined. AZM and MIN activities were assessed in the standard bacteriological medium CA-MHB (A-C), in the physiologically relevant amended tissue culture medium RPMI+ (D-F), and in the presence of 20% fresh human whole blood (G-I). (A) Bactericidal activity of AZM in CA-MHB. (B) Bactericidal activity of MIN in CA-MHB. (C) Fractional inhibition concentration (FIC) plot for AZM and MIN combinations in CA-MHB. (D) Bactericidal activity of AZM in RPMI+. (E) Bactericidal activity of MIN in RPMI+. (F) FIC plot for AZM and MIN combinations in RPMI+. (G) Bactericidal activity of AZM in 20% fresh human whole blood/ 80% RPMI. (H) Bactericidal activity of MIN in 20% fresh human whole blood/ 80% RPMI. (I) Fractional bactericidal concentration (FBC) plot for AZM and MIN combinations in 20% fresh human whole blood/ 80% RPMI. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. A representative plot is shown for each of the fractional inhibition/bactericidal graphs. Synergy is indicated by an FICI or FBCI of ≤0.5.