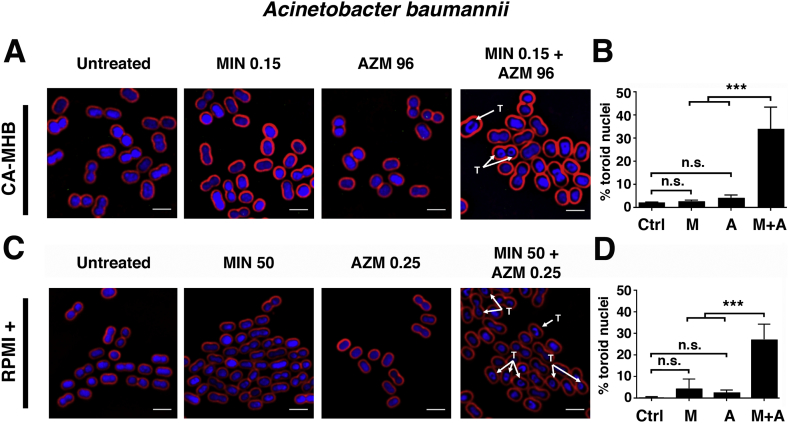
Fig. 4.
Bacterial cytological profiling (BCP) demonstrates augmented translation inhibition in MDR A. baumannii upon AZM + MIN cotreatment. A. baumannii strain AB5075 cells were grown in CA-MHB to a starting OD600 of 0.13 and treated for 2 h with MIN, AZM, or both drugs combined. Cells were strained for fluorescence microscopy with FM4–64 (red cell membrane dye), DAPI (blue DNA dye), and SYTOX-Green (green membrane-impermeable DNA dye, used as proxy for cell lysis). “T” denotes observed toroidal nuclei. (A) BCP was carried out for AZM and MIN both alone and in combination in CA-MHB. (B) The percentage of total cells counted, between 100 and 200 in at least 3 frames, with toroid nuclei for untreated and treated cultures in CA-MHB. (C) BCP was carried out for AZM and MIN both alone and in combination in RPMI+. (D) The percentage of total cells counted, between 100 and 200 in at least 3 frames, with toroid nuclei for untreated and treated cultures in RPMI+. BCP images are representative of 3 independent experiments. Percent total toroid containing cells is combined data from 3 independent experiments for each media type. Scale bar = 2 μm. For panels (B) and (D), statistical significance was calculated using a two-way ANOVA with ** ≤0.01 and *** ≤0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)