Fig. 1. NK cell immunity is required for the efficacy of combination MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy.
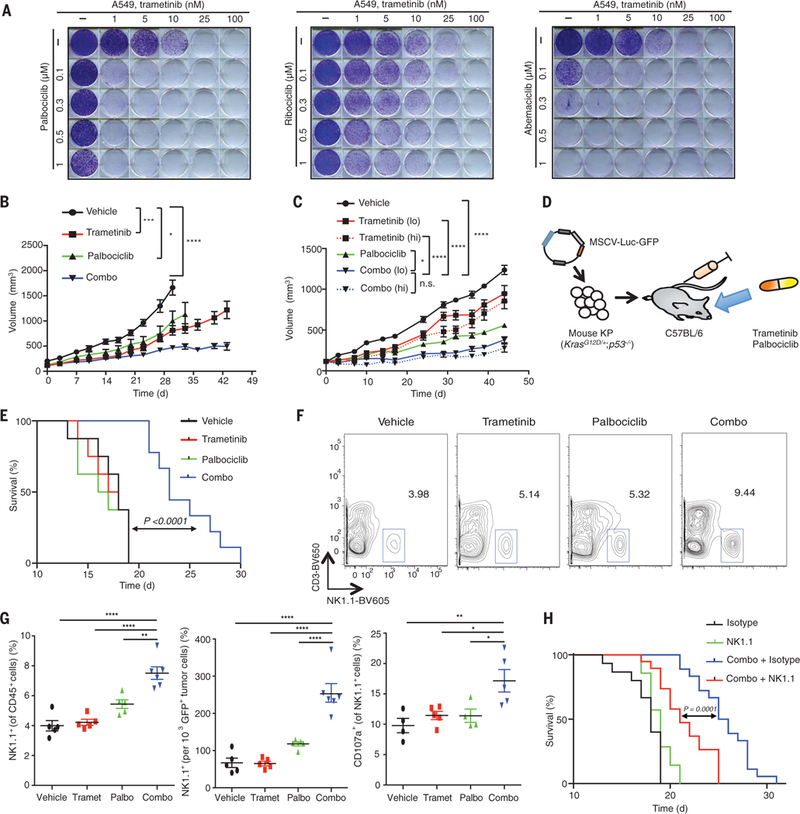
(A) Clonogenic assay of A549 lung cancer cells treated with MEK (trametinib) and/or various CDK4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, ribociclib, abemaciclib); representative of three biological replicates. (B) Tumor volumes of mice bearing KRAS-mutant MSK-LX27 PDX lung tumors treated with vehicle, trametinib (3 mg/kg body weight), palbociclib (150 mg/kg body weight), or both in combination (Combo) for indicated times (n = 5 mice per group). (C) Tumor volumes of mice bearing KRAS-mutant MSK-LX68 PDX lung tumors treated with vehicle, trametinib [1 mg/kg (lo) or 3 mg/kg (hi) body weight], palbociclib (150 mg/kg body weight), or both in combination for indicated times (n = 8 mice per group). n.s., not significant. (D) Syngeneic KP transplant lung cancer model. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of KP transplant mice treated with vehicle, trametinib (1 mg/kg body weight), palbociclib (100 mg/kg body weight), or both in combination (n ≥ 8 per group) (log-rank test). (F) Representative flow cytometry plots of NK cell populations in lung tumors from KP transplant mice treated for 1 week as in (E). (G) Percentage of NK cells within the CD45+ population (left), total NK cells relative to tumor cell number (middle), and percentage of CD107a+ degranulating NK cells (right) (n ≥ 4 mice per group). Palbo, palbociclib; Tramet, trametinib. (H) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of KP transplant mice treated with vehicle or combined trametinib (1 mg/kg body weight) and palbociclib (100 mg/kg body weight) and either an isotype control antibody (C1.18.4) or NK1.1-depleting antibody (PK136) (n ≥ 8 per group) (log-rank test). (B and C) Two-way ANOVA. (G) One-way ANOVA. Error bars, mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
