Figure 1.
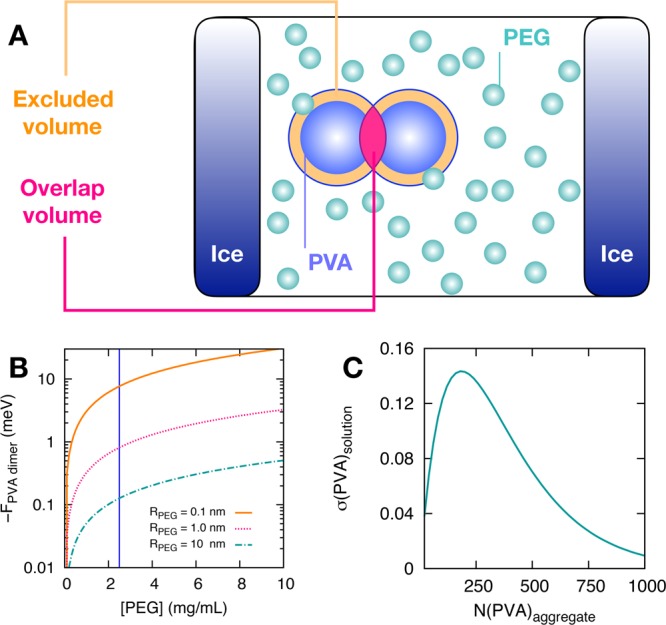
Depletion effects as the driving force for PVA aggregation in the presence of PEG particles. (A) Schematics of the origin of depletion forces: as the PEG particles cannot overlap with the PVA particles, the former cannot access a certain excluded volume around the latter. However, the excluded volume is reduced by the overlap volume created when two PVA particles get close enough. Thus, the aggregation of PVA increases the volume available to the PEG, which in turn leads to an entropic gain for the system. (B) Calculated free energy gain due to the aggregation of two PVA particles into a “dimer”, as a function of PEG concentration. (C) Calculated volume fraction σ(PVA)solution of PVA particles participating in PVA aggregates of size N(PVA)aggregate. The details of all these calculations are reported in the ESI.
