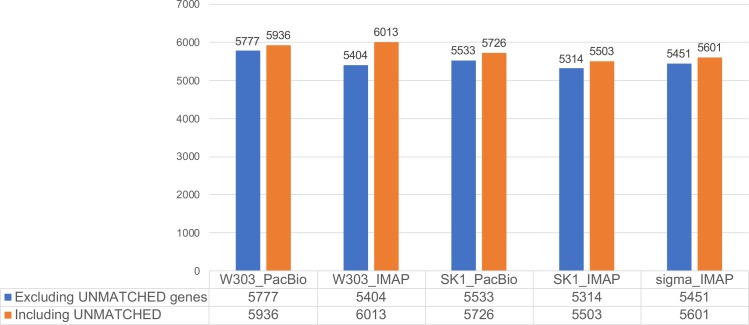
Fig 2. Assembly evaluation using gene annotation.
We validated the quality of our assemblies by measuring annotation completeness using AGAPE gene annotation [22]. AGAPE determines genes that are longer than 300 bases, and matches each gene to the NCBI database. If there are no genes found in the NCBI database or genes are partially matched less than a threshold value [22], they are marked as UNMATCHED, and parts of these genes are likely to be missed, because of assembly or annotation errors (note that although UNMATCHED genes could include novel genes, most are partially assembled genes in the S. cerevisiae strain genome [22]). We evaluated the annotation completeness for the assemblies of the genomes of three yeast strains: W303, SK1, and Sigma1278b. For W303 and SK1, we compared the gene annotation results of our IMAP assembly with that of the PacBio assembly using AGAPE.