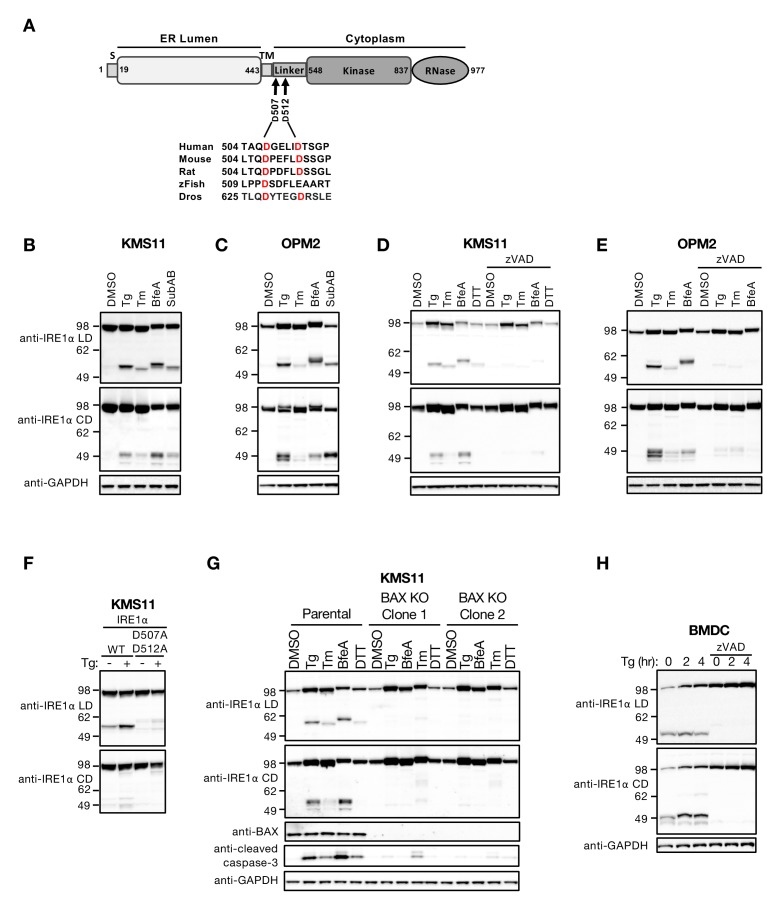
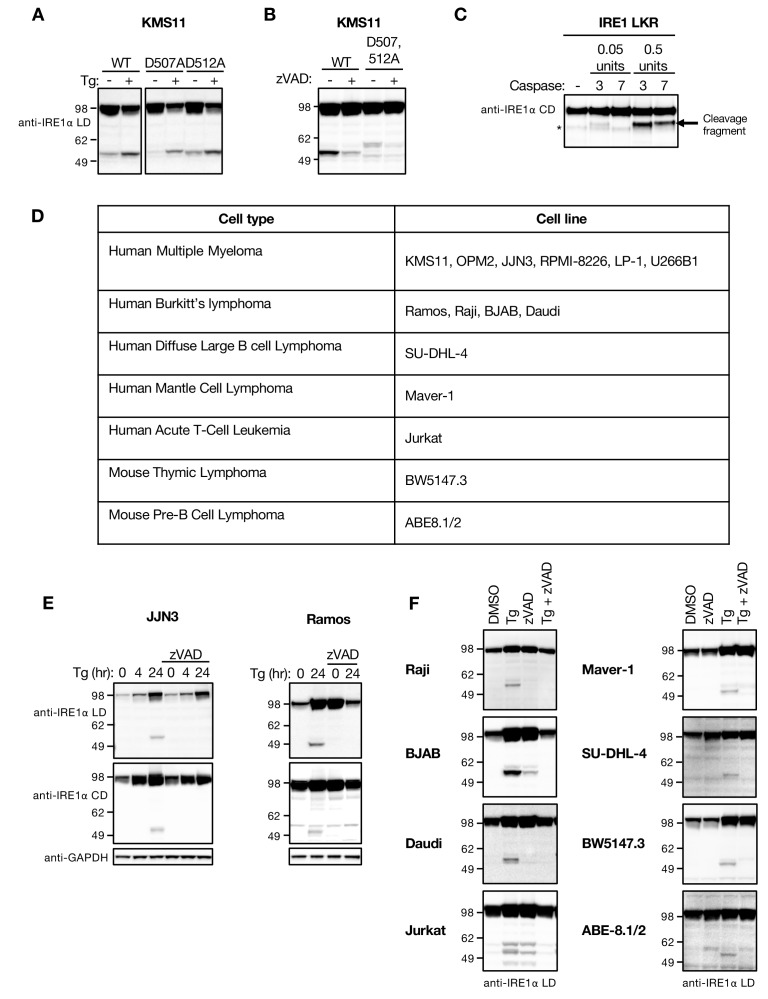
Figure 1. ER stress induces caspase-mediated cleavage of IRE1 in the cytoplasmic linker region.
(A) Schematic representation of the human IRE1 protein and comparison of the amino acid sequences surrounding the predicted caspase cleavage sites in the linker region of IRE1 from different species (zFish, zebrafish; Dros, Drosophila melanogaster). (B, C) KMS11 (B) or OPM2 (C) cells were treated with 100 nM Tg, 5 μg/ml Tm, or 0.2 μg/ml BfeA for 16 hr, or 0.3 μg/ml SubAB for 3 hr. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot (WB) with anti-IRE1α LD or anti-IRE1α CD antibody to detect the lumenal or cytoplasmic domains. (D, E) KMS11 (D) or OPM2 (E) cells were treated with 100 nM Tg, 5 μg/ml Tm, 0.2 μg/ml BfeA, or 1 mM DTT for 16 hr in the absence or presence of 20 μM zVAD. Samples were analyzed as in B for the presence of cleavage products. (F) A cDNA plasmid expressing either WT or doubly mutated IRE1 (D507A, D512A) was transiently transfected into KMS11 cells harboring CRISPR/Cas9-based IRE1 knockout. Cells were treated with either DMSO or 100 nM Tg for 16 hr and analyzed by WB as indicated. (G) Two independent KMS11 clones harboring CRISPR/Cas9-based BAX knockout were generated and validated for BAX deletion as compared to the parental cell line. Cells were treated with DMSO, 100 nM Tg, 0.5 μg/ml BfeA, 5 μg/ml Tm, or 1 mM DTT for 24 hr and analyzed by WB. (H) BMDCs were obtained from C57/BL6 mice and treated with 100 nM Tg in the absence or presence of 20 μM zVAD for the indicated times. Equal amounts of protein from cell lysates were analyzed by WB. B–H show representative results from at least three similar experiments. DMSO vehicle was used as control.