Figure 3.
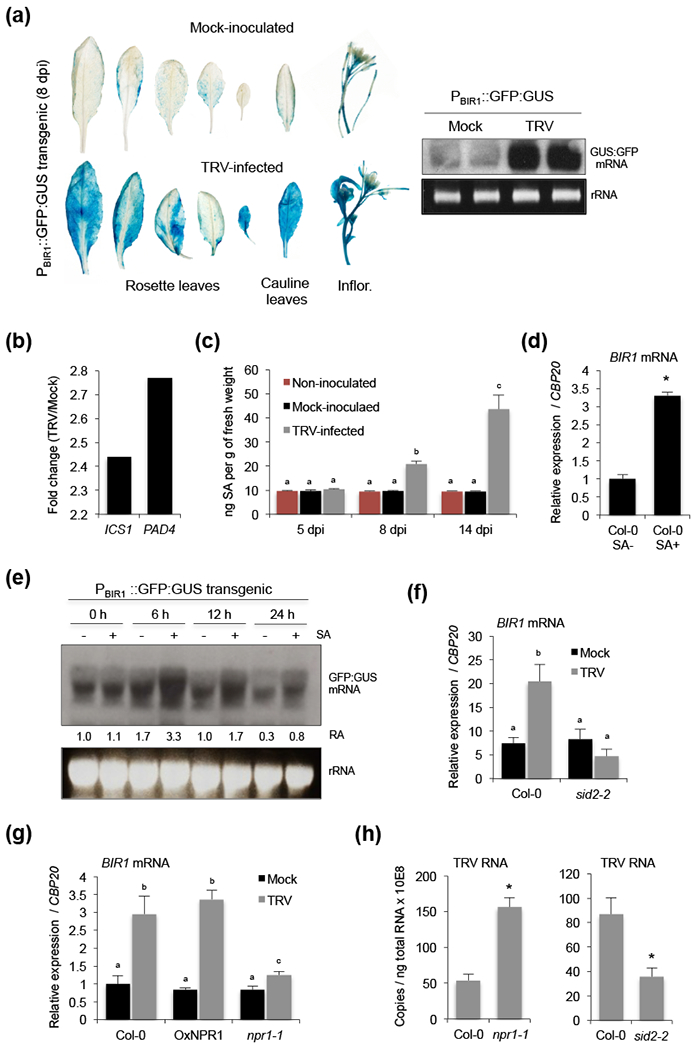
Salicylic acid (SA)-mediated transcriptional activation of BIR1 during viral infection. (a) Histochemical localization of GUS expression in mock-inoculated and TRV-infected transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing a GFP:GUS fusion protein under the control of the BIR1 promoter (left panel). Northern blot analysis was used to monitor the expression of GFP:GUS mRNA using a GFP-specific radiolabeled probe (right panel). Ethidium-bromide stained RNA (prior to transfer) is shown as loading control. (b) Differential expression of SA biosynthetic genes ICS1 and PAD4. Fold-change (log2) in TRV-infected plants relative to mock-inoculated ones detected using a CATMA microarray (GSE15557) (Fernandez-Calvino et al., 2014). (c) Time-course accumulation of SA determined by GC-TOF-MS in leaves from non-inoculated, mock-inoculated and TRV-infected Arabidopsis. Error bars represent SD from five independent biological replicates. (d) Accumulation of BIR1 transcripts in rosette leaves of wild type (Col-0) plants treated with (+) or without (−) SA as indicated. (e) Northern blot analysis of GFP:GUS mRNA in extracts from transgenic leaves treated with (+) or without (−) SA as indicated. Samples were collected at 0, 6, 12 and 24 h post-treatment and blots were hybridized with a GFP-specific DNA radiolabeled probe. Ethidium-bromide stained RNA (prior to transfer) is shown as loading control. The relative accumulation (RA) level for each sample is indicated (level in mock-treated plants at 0 h was arbitrarily set at 1.0). (f) Accumulation of BIR1 transcripts in mock-inoculated and TRV-infected rosette leaves of wild type and sid2-2 mutants at 8 days post-inoculation (dpi). (g) Accumulation of BIR1 transcripts in mock-inoculated and TRV-infected rosette leaves of wild type, NPR1 overexpressor and nrp1-1 mutants at 8 dpi. (h) Accumulation of TRV genomic RNA in rosette leaves of wild type, npr1-1 and sid2-2 mutants at 8 dpi. Relative expression levels were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to the CBP20 internal control. Unless otherwise indicated, error bars represent SD from three independent PCR measurements. Asterisks (Student’s t test) or different letters (one-way ANOVA) were used to indicate significant differences (P < 0.001). The experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results and one representative biological replicate is shown.
