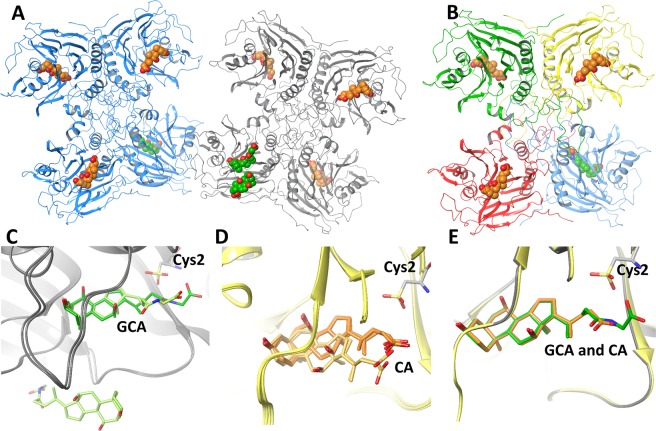
Figure 2.
The overall structures of GCA-soaked lsBSH complex. (A) It consists of two tetramers, which are composed of chains A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H. In each lsBSH tetramer, one monomer is in complex with the substrate, GCA (in green), while the remaining monomers are in complex with the product, CA (in orange). (B) The tetramer structure formed by chains E, F, G and H. Each monomer has different color. (C) The superimposition of lsBSH monomers bound to GCA. GCA is in green from chain F and light green from chain A. The monomer of chain A contains the second GCA molecule at the vicinity of the active site. (D) The superimposition of lsBSH monomers bound to CA. CA is in orange from chains B, D, G and H and light orange from chains C and E. (E) The superimposition of lsBSH monomers bound to GCA and CA from chains F and B. The catalytic cysteine residue, Cys2 found in the oxidized form is shown in stick representation.