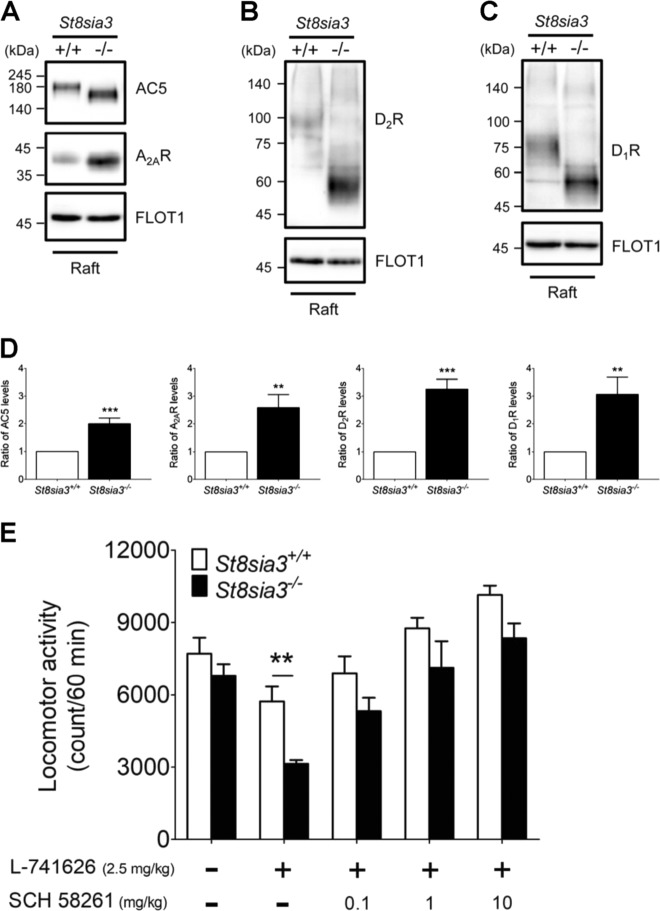
Fig. 5. St8sia3 disruption increased the amount of substrates distributed in lipid rafts and altered the locomotor activities of mice treated with A2AR and D2R antagonists.
a–c Lipid raft membrane regions in the striatum of WT (+/+) and St8sia3-KO (−/−) mice were isolated using a nondetergent method and analyzed for substrate distribution by immunoblotting. AC5, A2AR, D2R, and D1R were all dispensed in fraction 3 (raft) along with FLOT1, a well-characterized lipid raft marker. d Quantitative densitometry analysis was used to measure the intensities of substrates in the lipid raft fractions. ST8SIA3 deficiency significantly increased the amounts of AC5, A2AR, D2R, and D1R in lipid rafts. n = 15 for each genotype used for seven independent experiments. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, compared with WT control (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). All values are presented as the means ± S.E.M. e The A2AR antagonist SCH 58261 reversed the effects of the D2R antagonist L-741626 on locomotor activity. L-741626 reduced locomotor activity. The difference between WT and St8sia3-KO mice was observed at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg. SCH 58261 reversed the differences observed between St8sia3-and WT mice at concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg. n = 8 for each genotype. **P < 0.01, compared with the WT control (two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests). All values are presented as the means ± S.E.M