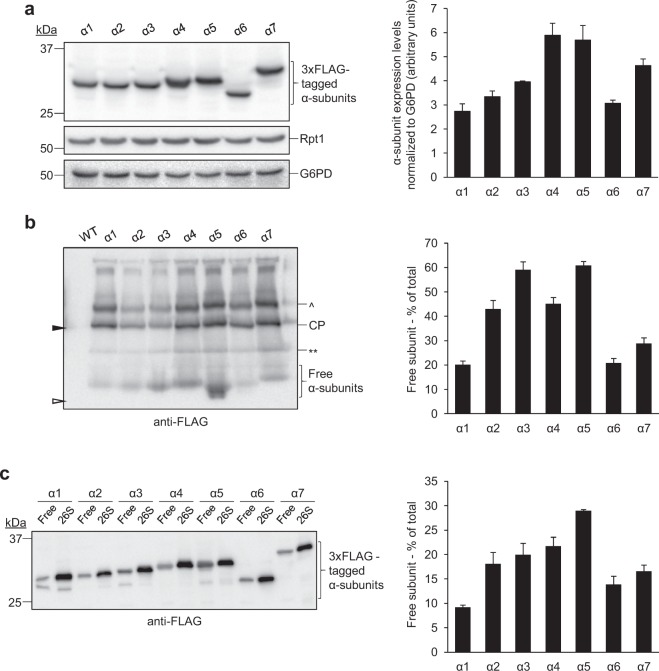
Figure 7.
Proteasome subunit α1 is stoichiometrically limiting for proteasome α-ring assembly. (a) Whole cell lysates of yeast strains expressing the indicated 3xFLAG-tagged α-subunits from their chromosomal loci were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against FLAG, Rpt1, or G6PD (loading control). Quantification of α-subunit expression levels, normalized to the G6PD loading control, is shown to the right (n = 3; error bars = s.e.m.). Full-length blot is presented in Supplementary Fig. S8. (b) Cell extracts prepared from yeast strains expressing 3xFLAG-tagged α-subunits from their chromosomal loci were separated via blue native PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against FLAG. Samples were prepared under conditions favoring dissociation of the RP from CP from the 26S proteasome to directly examine subunit abundance in the context of the CP only. Triangles denote migrations of purified CP (filled) and a 20 kDa standard (open). Quantification of the percentage of free α-subunit (shown to the right) was determined by dividing the band corresponding to free α-subunit by the sum of the free and assembled (CP band) subunit abundance for each lane (n = 4; error bars = s.e.m.). ^, Blm10-CP; **, CP assembly intermediate. Full-length blot is presented in Supplementary Fig. S8. (c) Cell extracts prepared from yeast strains expressing the indicated 3xFLAG-tagged α-subunits from their chromosomal loci were fractionated by gel filtration chromatography. Peak fractions corresponding to free α-subunits and 26S proteasomes were separated via SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against FLAG. The percentage of free α-subunit (shown to the right) was determined by dividing the band corresponding to free subunit (free) by the sum of the free and 26S band intensities for each lane. (n = 8; error bars = s.e.m.). Full-length blot is presented in Supplementary Fig. S8.