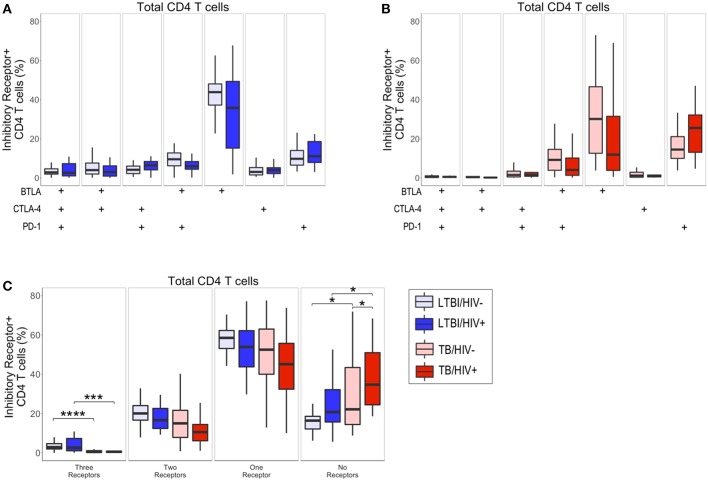
Figure 2.
Active TB disease is associated with reduced inhibitory receptor co-expression on total CD4 T cells. PBMC from HIV-uninfected and HIV-infected individuals with LTBI (n = 32 and n = 22, respectively) and active TB (n = 37 and n = 19, respectively) were analyzed by flow cytometry for expression of the inhibitory receptors BTLA, CTLA-4, and PD-1 on total CD4 T cells. (A,B) The frequencies of total CD4 T cells expressing each combination of BTLA, CTLA-4, and PD-1 are shown for individuals with LTBI (A) and active TB (B). (C) Summary data representing the proportion of total CD4 T cells expressing three, two, one, or no inhibitory receptors from HIV-uninfected and HIV-infected individuals with LTBI and active TB. Boxes represent the median and interquartile ranges; whiskers represent the 5th and 95th percentiles. Differences in the proportion of CD4 T cells expressing each inhibitory receptor population between HIV-uninfected and HIV-infected individuals (A,B) were assessed using a Mann-Whitney U test. Differences among groups in the number of inhibitory receptors expressed by CD4 T cells in panel C were assessed using a Kruskal-Wallis test, with p-values adjusted for multiple comparisons using Dunn's post-test. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.