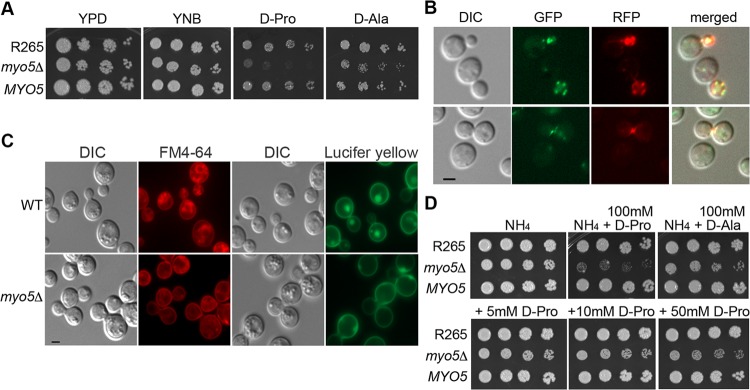
FIG 1.
Identification of MYO5 function. (A) MYO5 is important for d-proline utilization. Cells of the wild type, the myo5Δ mutant, and the myo5Δ complemented strain (MYO5) were serially diluted and spotted on the indicated media. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days and photographed. (B) Myo5 is colocalized with actin cortical patches. Myo5 was tagged with green fluorescent protein (GFP) (green color). Actin was visualized with Lifeact-RFP (red color). Fluorescent and differential interference contrast (DIC) images were taken from log-phase cells. (C) MYO5 is involved in endocytosis. Cells were stained with FM4-64 to determine membrane internalization (DIC and FM4-64 columns) or stained with Lucifer yellow to determine fluid phase endocytosis (DIC and Lucifer yellow columns). For FM4-64 staining, cells were stained with 16 μM FM4-64 on ice for 15 min, washed, and incubated in YEPD for 80 min before imaging. Bar = 2 μm. WT, wild type. (D) d-Amino acids are toxic to the myo5Δ mutant. Cells were serially diluted and spotted on media containing 10 mM ammonium sulfate (NH4) with or without supplementation with 100 mM d-proline or d-alanine (top row). Cells were also spotted on NH4 media supplemented with 5, 10, or 50 mM d-proline (bottom row). Plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days and photographed.