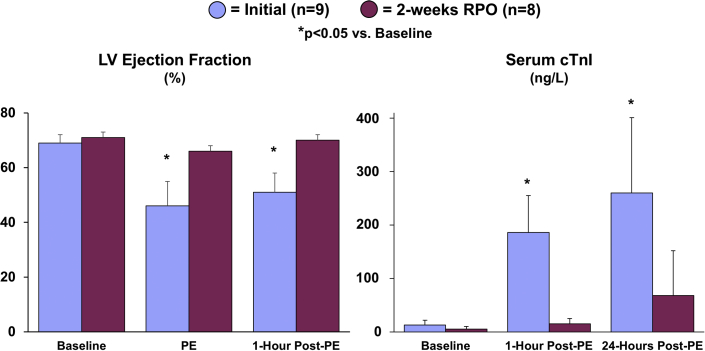
Figure 2.
Cardiac Adaptations to RPO Prevent Acute Stretch-Induced Stunning and Myocyte Injury During a Transient Elevation in Afterload
The attenuation of LV distension during PE infusion after RPO was associated with a preserved LV ejection fraction and the absence of a significant elevation in serum cardiac troponin I (cTnI) concentrations, indicating that RPO led to an adaptive reduction in LV compliance that protected the heart from stretch-induced stunning and myocyte injury during PE-mediated pressure overload. Values are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus baseline. Representative videos of short-axis echocardiograms that illustrate the LV response to PE at the initial study (Supplemental Videos 1A, 1B, 1C) and after 2-weeks of RPO (Supplemental Videos 2A, 2B, 2C) are included in the Supplemental Appendix. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.
Video Files 1A-1C: Example Left Ventricular Short-Axis Echocardiograms at the Initial Study
Short-axis echocardiograms from the initial study demonstrate normal left ventricular systolic function at rest (arterial blood pressure (BP): 124/78 mmHg; Video 1A), followed by marked dilatation and systolic dysfunction during phenylephrine (PE) infusion (arterial BP: 216/155 mmHg; Video 1B) that persists following cessation of PE despite normalization of arterial BP (arterial BP: 125/86 mmHg; Video 1C).
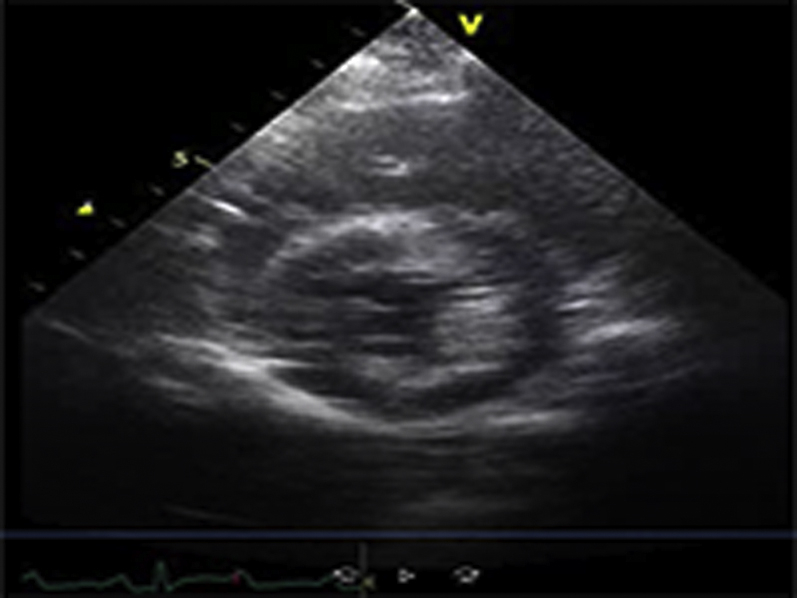
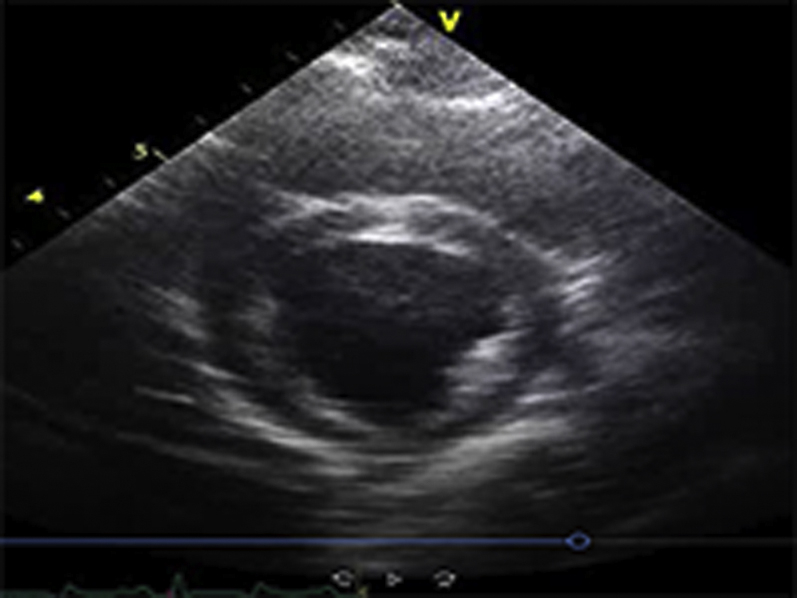
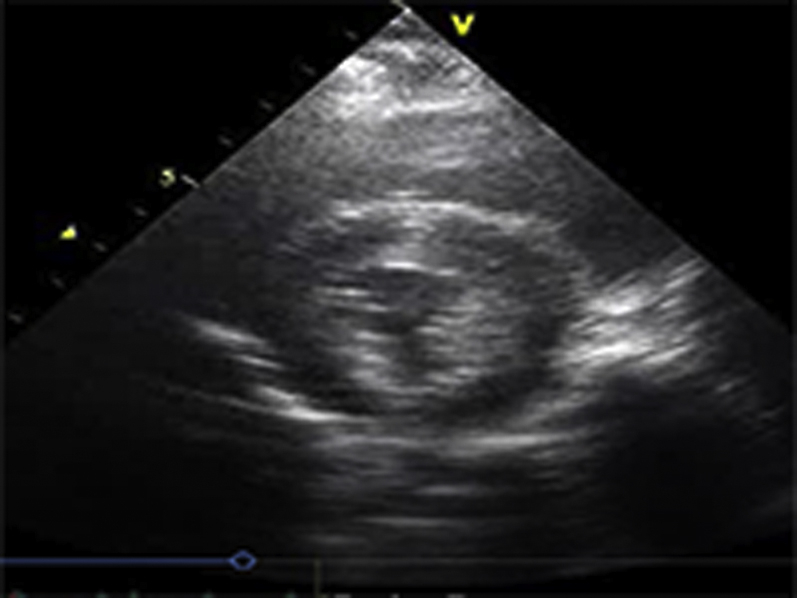
Video Files 2A-2C: Example Left Ventricular Short-Axis Echocardiograms After 2-weeks of Repetitive Pressure Overload
Short-axis echocardiograms from the same animal shown in Video Files 1A-1C obtained after 2-weeks of RPO demonstrate normal left ventricular systolic function at rest (arterial blood pressure (BP): 102/61 mmHg; Video 2A) as well as during (arterial BP: 230/154 mmHg; Video 2B) and after (arterial BP: 132/82 mmHg; Video 2C) phenylephrine (PE) infusion despite a similar arterial BP response to PE at both studies.
*Note: All example echocardiograms were collected from the same animal subject.