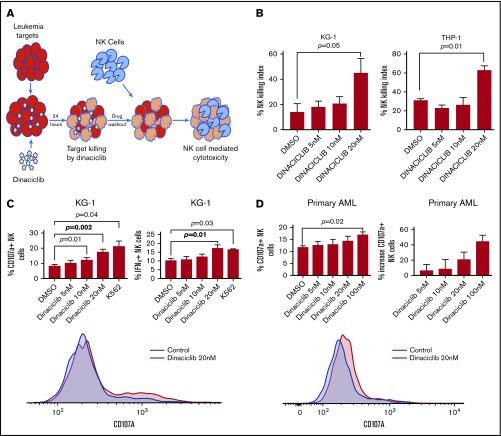
Figure 1.
Dinaciclib enhances NK-cell activation and cytotoxicity against human AML targets. (A) Study scheme for NK-cell killing and activation assay. (B) NK-cell–killing assay. KG-1 and THP-1 cell lines were incubated with dinaciclib for 24 hours. After drug washout, NK cells (an E:T ratio of 2:1) or media were incubated with targets for 24 hours. The NK-killing index (percentage) was calculated by comparing the percentage of AML targets killed with drug treatment combined with donor NK cells relative to drug treatment alone. (C-D) Leukemia targets were incubated with dinaciclib overnight. Healthy donors’ PBMCs were added to and incubated with targets for 4 hours with an E:T ratio of 2:1. CD107a and/or IFNγ of NK cells were measured by flow cytometry. (C) NK-cell activation against KG-1. K562 serves as a positive control. (D) NK-cell activation against primary AML samples. The data represent replicates using NK cells from 4 healthy donors and representative histograms are shown at the bottom. Error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.