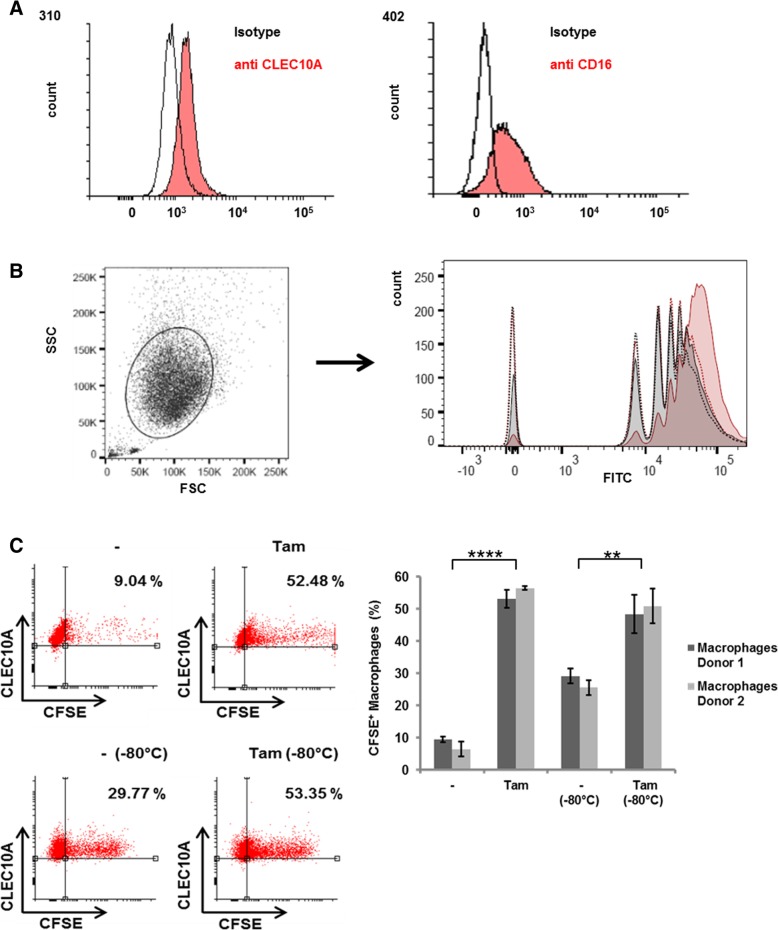
Fig. 4.
Increased phagocytosis of CLEC10A ligands by macrophages. a Surface expression of CLEC10A and CD16 on macrophages derived from human PBMC of healthy donors after differentiation by M-CSF. Subsequent blocking of Fc-receptors, macrophages were stained by using an APC labeled anti-CLEC10A antibody and a PerCP-Cy5 labeled anti CD16-antibody, respectively (red filled histograms). Fluorescence intensity was compared to cells stained with the corresponding isotype controls (non-filled histogram). b Increased uptake of fluorospheres carrying Tn-antigen (red, filled histogram) in macrophages compared to control beads carrying the spacer (grey, filled histogram). As a control for calcium-dependent internalization, the uptake of Tn- and control beads was investigated in the presence of EDTA (red dotted line and grey dotted line). The different peaks are due to the uptake of distinct numbers of particles per macrophage. c Macrophages from two independent donors were incubated with CFSE-labelled MCF7 cells treated with 4 μM Tamoxifen (Tam) for 48 h or with cells treated with solvent control (−). To analyze engulfment of dead cells by macrophages, aliquots of labelled cells were treated by freeze and thaw cycles (− 80 °C). The amount of CFSE and CLEC10A double positive cells were measured by flow cytometry. Dot plots of four representative measurements are given. Error bars depict the standard deviation of three technical replicates. p values: donor 1 – vs. Tam = 0.000014; donor 1 – (− 80 °C) vs. Tam (− 80 °C) = 0,0061; donor 2 – vs. Tam = 0.0000035; donor 2 – (− 80 °C) vs. Tam (− 80 °C) = 0.0018