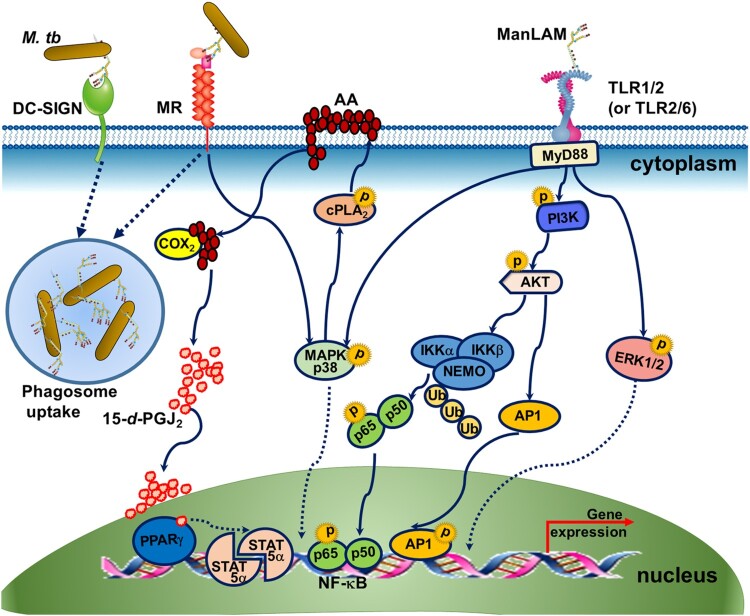
Figure 2.
The signalling pathway induced by ManLAM. (1) Recognition of ManLAM by MR and DC-SIGN mediates the phagocytosis of M.tb. (2) MR mediates the enhanced expression of the transcription regulatory factor PPAR-γ and the subsequent upregulation of transcription of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-5α. ManLAM binding to MR leads to activation of MAPK-p38-mediated cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), which drives the release and hydrolysis of arachidonic acids (AA) from the plasma membrane to generate the ligand (15-deoxy-Δ12,14 PGJ2, 15-d-PGJ2) for PPARγ. PPARγ activation leads to the activation of STAT-5α. (3) The TLR2 signalling pathway is triggered by ManLAM. ManLAM recognition by TLR1/2 and TLR2/6 drives the MyD88-dependent pathway. MyD88 activation results in activation of NF-κB, AP-1, MAPK p38 and ERK1/2. Phosphorylation of PI3 K and AKT is required for NF-κB and AP-1 activation. Lys48 (K48) -linked ubiquitination of NEMO is also involved in the upstream signal transduction of NF-κB.