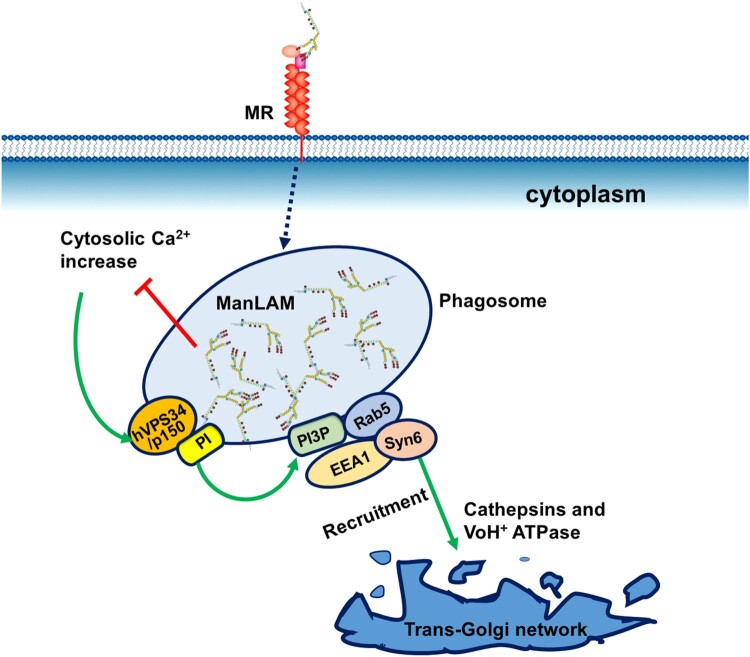
Figure 3.
Inhibition of phagosome maturation by ManLAM. The phagosome-lysosome fusion process is classically dependent on cytosolic Ca2+ increase. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent PI3-kinase hVPS34 and its modulatory subunit p150 generate phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) on the phagosomal membrane. PI3P mediates the recruitment of the membrane tethering protein early endosome autoantigen 1(EEA1) to the phagosome. EEA1 is essential for phagosome maturation by directly interacting with syntaxin-6 (Syn6), which is involved in the delivery of cathepsins (lysosomal hydrolases) and VoH1-ATPase from the trans-Golgi network to the phagosome. ManLAM inhibits cytosolic-Ca2+ increase and thereby blocks the successive steps, resulting in the prevention of lysosomal fusion and acidification.