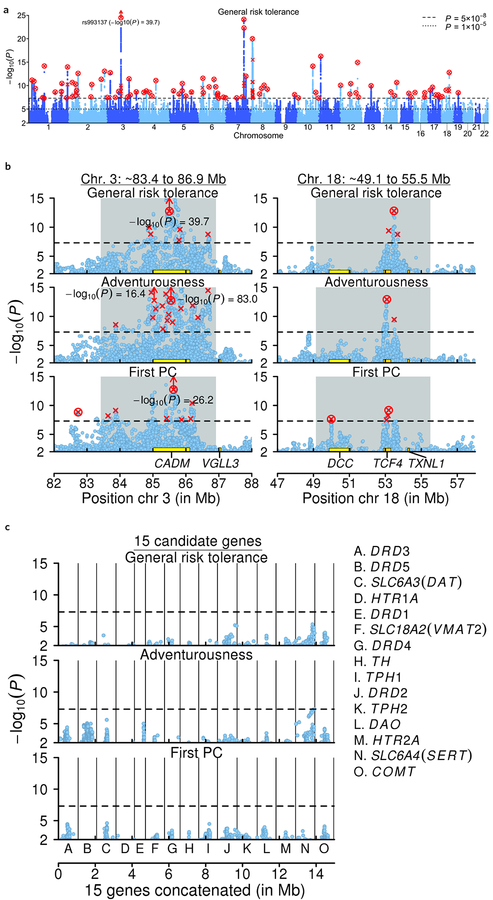
Figure 1 |. Manhattan plots.
In all panels, the x-axis is chromosomal position; the y-axis is the GWAS P value on a −log10 scale (based on a two-tailed z-test); each lead SNP is marked by a red “×”; each conditional association is marked by a red “o”; and each SNP that is both a lead SNP and a conditional association is marked by a red “⊗”. a, Manhattan plots for the discovery GWAS of general risk tolerance (n = 939,908). b, Local Manhattan plots of a long-range LD region on chromosome 3 and a candidate inversion on chromosome 18 that contain lead SNPs for all seven of our GWAS. The gray background marks the locations of long-range LD or candidate inversion regions. c, Local Manhattan plots of the areas around the 15 most commonly tested candidate genes in the prior literature on the genetics of risk tolerance. Each local plot shows all SNPs within 500 kb of the gene’s borders that are in weak LD (r2 > 0.1) with a SNP in the gene. The 15 plots are concatenated and shown together in the panel, divided by the black vertical lines. The 15 genes are not particularly strongly associated with general risk tolerance or the risky behaviors, as can be seen by comparing the results within each row across panels b and c (the three rows correspond to the GWAS of general risk tolerance, adventurousness (n = 557,923), and the first PC of the four risky behaviors (n = 315,894)).