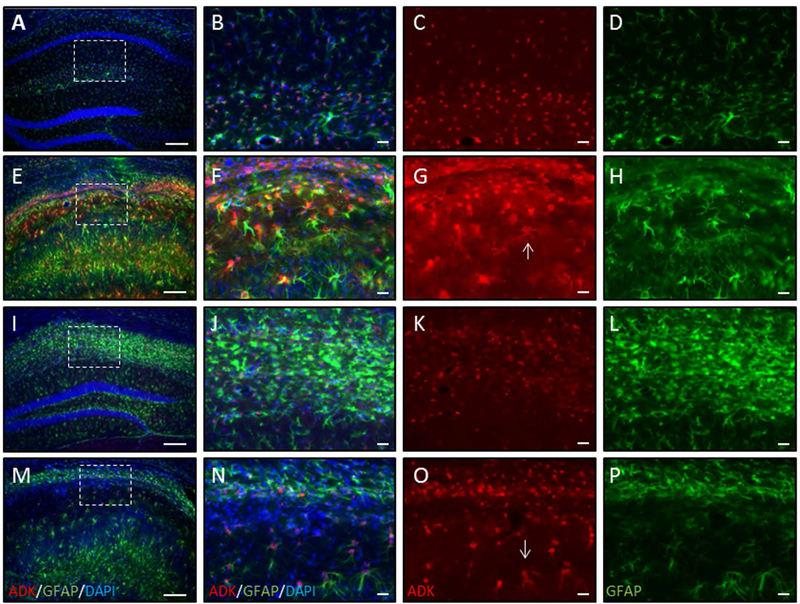
Figure 4. Transient systemic treatment with 5-ITU reduces ADK overexpression in mice protected from epilepsy.
Adult male C57BL/6 mice were injected with unilateral intrahippocampal kainic acid (KA) received 1.6mg/kg 5-ITU or 20% DMSO vehicle (Veh) injections (i.p., b.i.d.) from 3–8d post injury. Control mice had intrahippocampal saline (Sal) injection followed by Veh injections. Tissue was harvested at 9wk post intrahippocampal injection. ADK (red), GFAP (green) and DAPI (blue) immunofluorescence in coronal ipsilateral hemisphere of Sal-Veh (A–D), KA-Veh (E–H) and KA-5-ITU-Protected (I–L) and KA-5-ITU-Not protected (M–P). (A,E,I,M) Low magnification images. Note that DAPI staining shows that in the KA-Veh (E), KA-5-ITU-Protected (I) and KA-5-ITU-Not protected (M) mice there is CA1 thinning, but in only the KA-Veh and KA-5-ITU-Not protected mice there is compression of the CA1 subfield and granule cell dispersion. Higher resolution images of the CA1 subfield demarcated by the white box in Sal (B–D), KA-Veh (F–H), KA-5-ITU-Protected (J–L), and KA-5-ITU-Not protected (N–O) mice. (B–D) Sal hippocampus has ADK confined largely to the nucleus and perinuclear region of GFAP stained astrocytes. (F–H) KA-Veh hippocampus has increased ADK expression that is present in the cytoplasm (arrow in G) of reactive astrocytes that have increased GFAP immunoreactivity. (J–L) KA-5-ITU-Protected hippocampus has an increase in GFAP immunoreactive astrocytes that are ADK positive. (N–P) KA-5-ITUnon-protected hippocampus has an increase in GFAP immunoreactive astrocytes with increased ADK expression (arrow in O). Scale bars = 150µm (A,E,I,M); 25µm (B–D,F–H,J–L,N–P).