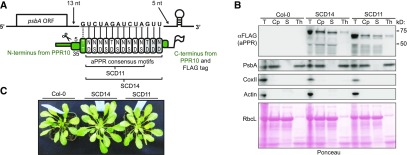
Figure 1.
Overview of Artificial PPR Proteins Designed to Bind the psbA 3ʹ UTR.
(A) Protein design. SCD11 and SCD14 were designed to bind the indicated 14- or 11 (underlined)-nucleotide (nt) sequence in the 3ʹ UTR of the psbA mRNA in Arabidopsis. The targeted sequence begins 13 nucleotides downstream of the stop codon and ends five (SCD14) or eight (SCD11) nucleotides upstream of the 3ʹ-terminal stem-loop in the psbA mRNA. SCD14 and SCD11 contain 13 and 10 consensus PPR motifs, respectively, flanked by sequences from PPR10 (green). The motifs that are found in SCD14, but not in SCD11, are marked in gray. The specificity-determining amino acids (Barkan et al., 2012) (positions 5 and 35 according to the nomenclature in Yin et al., 2013) are indicated, and each repeat is aligned with its nucleotide ligand. The PPR10-derived sequence at the N terminus includes a chloroplast targeting sequence and PPR10’s first PPR motif, which has a noncanonical specificity code (dotted line). The targeting sequence is cleaved after import into the chloroplast (scissors). Both proteins contain a C-terminal 3xFLAG tag. ORF, open reading frame.
(B) Immunoblots demonstrating chloroplast-localization of SCD11 and SCD14. Chloroplasts (Cp) were isolated from total leaf (T) of wild-type (Col-0) and transgenic Arabidopsis plants and fractionated to generate thylakoid membrane (Th) and soluble (S) fractions. Aliquots representing an equivalent amount of starting material were probed to detect markers for cytosol (Actin), mitochondria (Cox II), and thylakoid membranes (PsbA). The aPPR proteins were detected with anti-FLAG antibody. The Ponceau S–stained filter is shown below to demonstrate the partitioning of the chloroplast stromal protein RbcL (the large subunit of Rubisco).
(C) Visible phenotype of transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing SCD14 and SCD11. Col-0 is the wild-type progenitor of the transgenic lines.