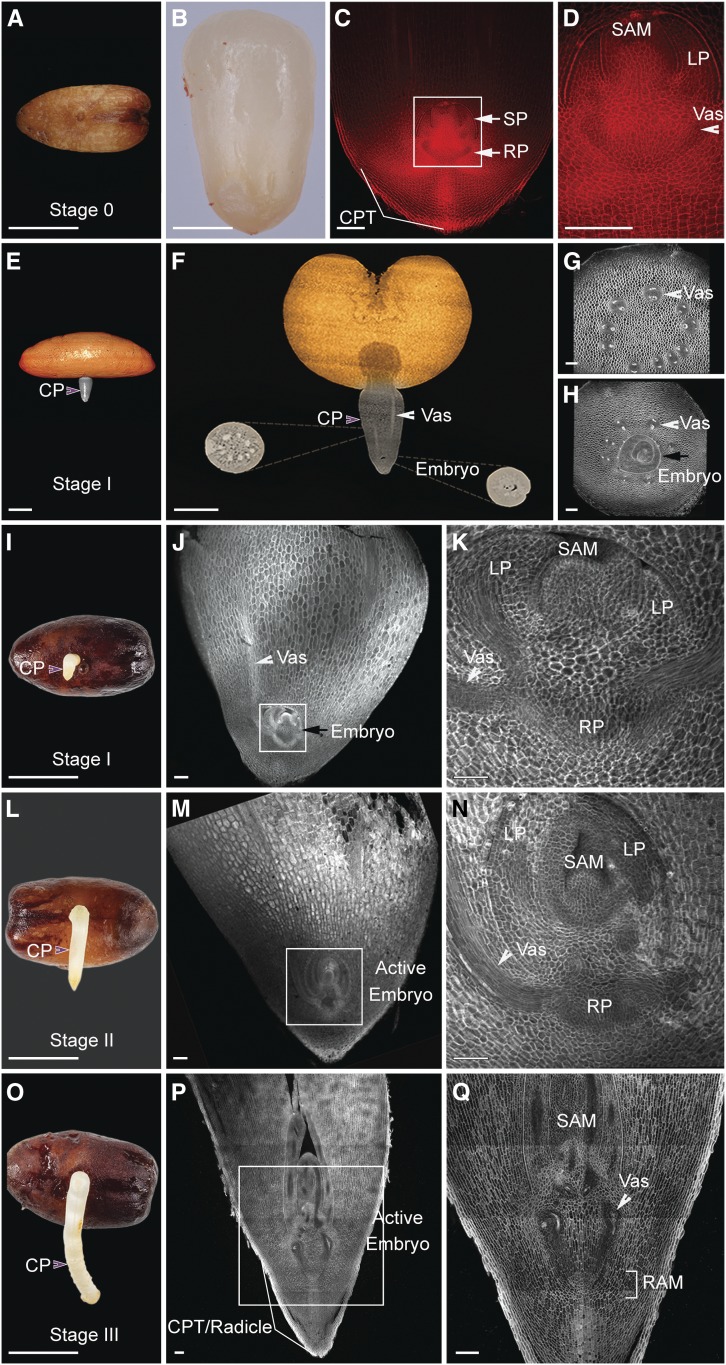
Figure 2.
Growth Dynamics during Germination in Date Palms.
(A) Date palm seed containing the embryo. Bar = 1 cm.
(B) Embryonic sac dissected from the seed (n = 20). Bar = 0.5 cm.
(C) and (D) Longitudinal section of dissected embryo sac (see [C] and [D]) stained with mPS-PI (n = 20). The white arrows indicate root and shoot axes in (C). Bar in (C) and (D) = 100 µm.
(E) and (F) 3D image of germinated date palm at stage I imaged with XμCT (n = 3). Bar in (E) = 5 mm; bar in (F) = 2 mm.
(G) and (H) Confocal images of cotyledonary petiole sections taken at the same stage as in (F). The section in (G) at the top part, which does not include the embryo; the section in (H) includes a transverse view of the embryo (n = 15). Bar in (G) and (H) = 100 µm.
(I) to (Q) Date palm growth at 1 to 4 weeks after germination (n = 25). (I), (L), and (O) are macrophotographs; (J), (K), (M), (N), (P), and (Q) are confocal images of longitudinal vibratome sections with the cell walls stained with SCRI Renaissance 2200 (n = 10). White arrowheads point to the vasculature (Vas); purple arrowheads point to the cotyledonary petiole (CP). The black arrows in (H) and (J) indicate the embryo. Images are representative of the total number (n) of seedlings that were studied. (D), (K), (N), and (Q) are insets of (C), (J), (M), and (P), respectively. Bar in (I), (L), and (O) = 1 cm; bar in (M) and (P) = 100 µm; bar in (K) and (N) = 50 µm
CPT, cotyledonary petiole tip; LP, leaf primordia; RAM, root apical meristem; RP, root pole; SP, shoot pole.