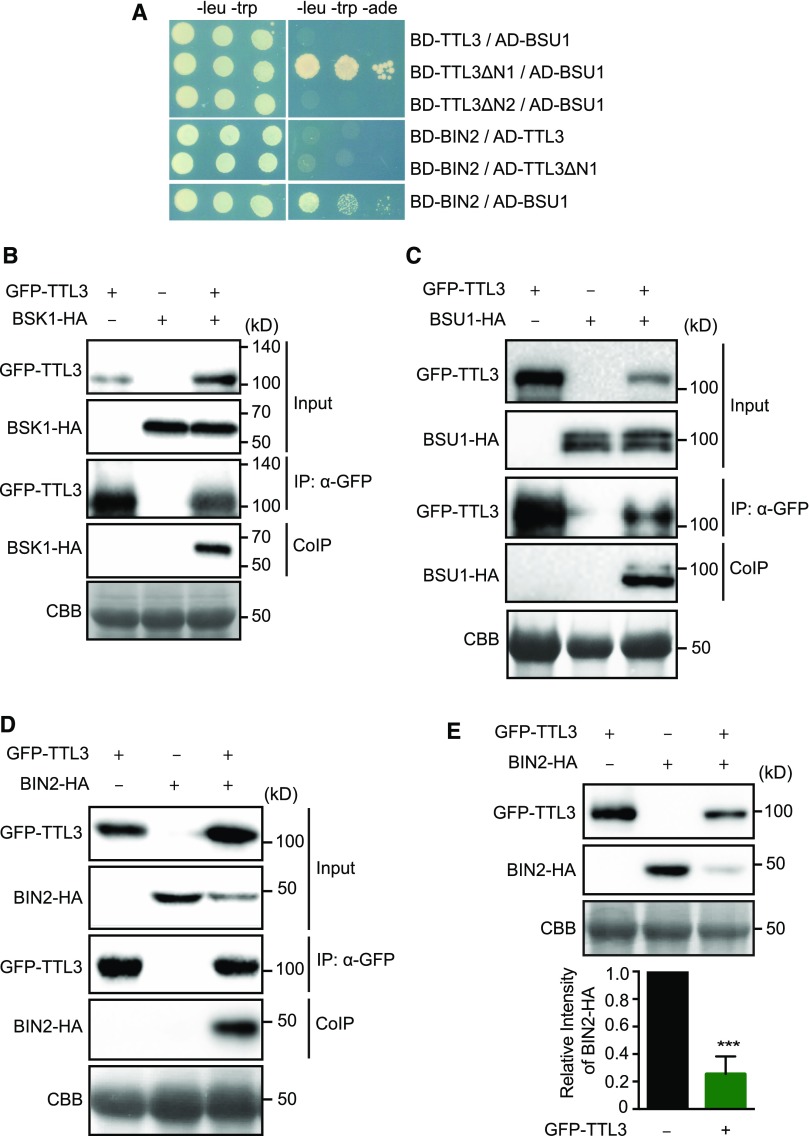
Figure 5.
TTL3 Associates with BSK1 and BIN2 and Directly Interacts with BSU1.
(A) Yeast-two-hybrid assays to determine the interaction of full-length TTL3, the TTL3 fragment TTL3ΔN1 (amino acids 204 to 691), and the TTL3 fragment TTL3ΔN2 (amino acids 371 to 691) with BIN2 and BSU1. Growth on plasmid-selective media (left column) and interaction-selective media (lacking adenine [-ade], right column) are shown.
(B) BSK1 co-immunoprecipitates with TTL3. BSK1-HA, and GFP-TTL3 were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana. GFP-TTL3 was IP with anti-GFP Trap beads. Total (input), IP, and CoIP proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Equal loading was confirmed by Coomassie blue staining (CBB) of input samples. GFP-TTL3 and BSK1-HA were detected with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibody, respectively.
(C) BSU1 co-immunoprecipitates with TTL3. GFP-TTL3 and BSU-HA proteins were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana, IP, and analyzed as described in (B). GFP-TTL3 and BSU1-HA were detected with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies, respectively.
(D) BIN2 co-immunoprecipitates with TTL3. BIN2-HA and GFP-TTL3 proteins were expressed in N. benthamiana, IP, and analyzed as described in (B). GFP-TTL3 and BSU1-HA were detected with anti-GFP and anti-HA, respectively.
(E) TTL3 promotes BIN2 depletion. BIN2-HA with and without GFP-TTL3 was expressed in N. benthamiana. Protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting. Equal loading was confirmed by Coomassie blue staining (CBB) of input samples. GFP-TTL3 and BIN2-HA were detected with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibody, respectively. Bottom graph represents the signal density of BIN2-HA coexpressed with or without GFP-TTL3 in N. benthamiana was quantified based on the six biological repeats. The immunoblot signal intensity of BIN2-HA coexpressed with GFP-TTL3 was normalized to the immunoblot signal intensity of BIN2-HA coexpressed with an empty vector. Asterisks indicate statistical differences as determined by the unpaired t test (***P ≤ 0.001).