Fig. 1.
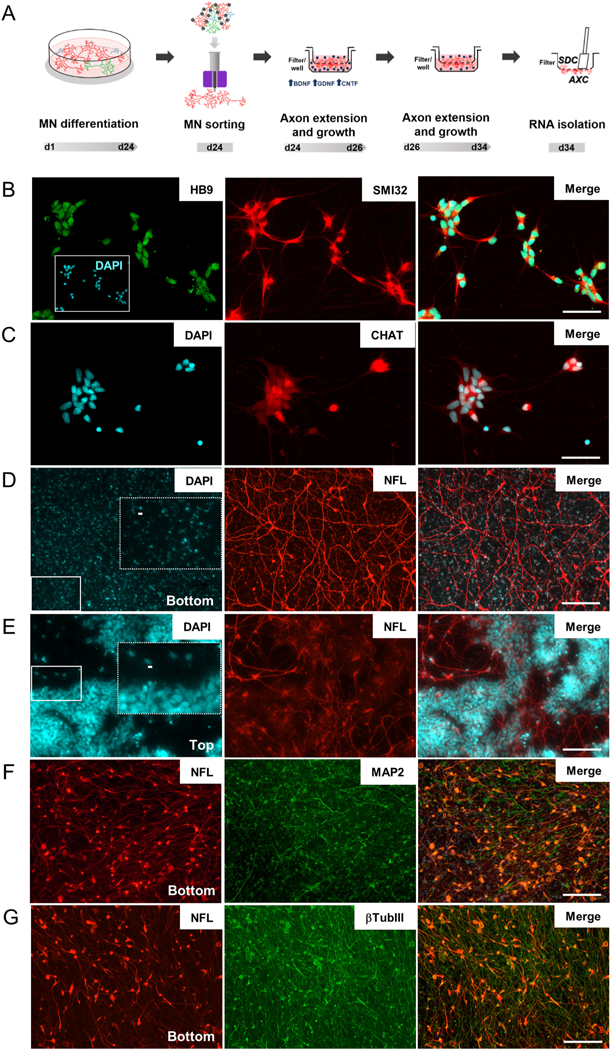
Isolation of axons from iPSC-derived motor neurons. (A) Timeline showing motor neuron differentiation protocol and separation of cell compartments for RNA isolation. Representative images of sorted motor neurons stained for (B) HB9 and SMI32 and (C) CHAT. (D & E) Permeable inserts bearing a 1.0-μm porous membrane were used to obtain large amounts of (D) enriched axonal material from iPSC-derived motor neurons. No neuronal nuclei were identified on DAPI staining at filter-bottom compartment, as opposed to the (E) numerous nuclei observed in the filter top. Dashed rectangles in D and E are zoomed images from fields indicated by solid rectangles showing (D) blue auto fluorescence of filter pores in bottom compartment and (E) nuclei staining in top compartments. Scale bar 5 μm. (F & G) Representative images of bottom compartments showing that neuronal projections (β-TubIII) are mainly composed of axons (NFL) and few dendrites (MAP2). HB9: Homeobox HB9; SMI32: neurofilament heavy chain; CHAT: choline acetyltransferase; NFL: neurofilament light chain; MAP2: microtubule associated protein 2; βTubIII: Tubulin, beta 3 class III. Scale bar 100 μm.
