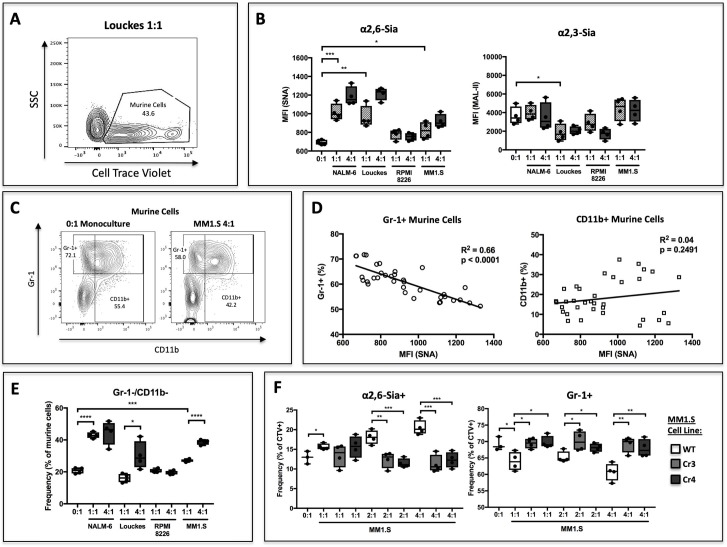
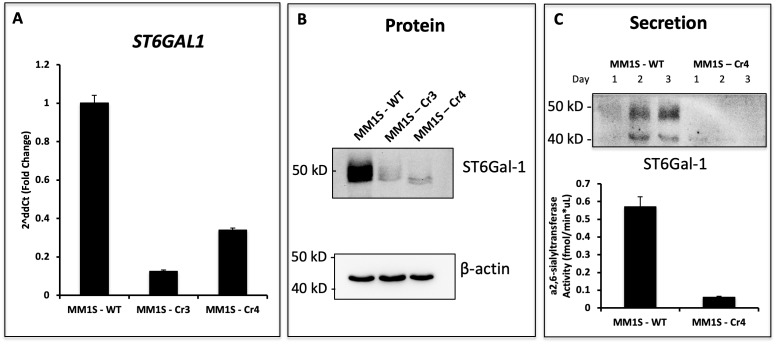
Figure 3. B cells modify HSPC SNA reactivity and Gr-1 expression in co-culture.
Human B lymphoblastoid cell lines were co-cultured with CellTrace Violet-labeled murine St6gal1KO c-kit+ bone marrow cells for 3 days with SCF, IL-3, G-CSF, TPO, and Flt-3 at indicated ratios of 1:1, 2:1, or 4:1. (A) Resolution of B cells and murine HSPCs by flow cytometry, with HSPCs staining positive for CellTrace Violet. (B) Levels of SNA and MAL-II reactivity on the HSPCs in monoculture or co-culture with indicated B cells. (C) Flow cytometric separation of CD11b+ and Gr1+ cells from murine HSPCs, after 3 days of monoculture (left) or co-culture (right) with MM1.S myeloma cells at 4:1 ratio. (D) Correlation between murine cell SNA reactivity and frequency of Gr-1+ or CD11b+ cells (expressed as % of total CellTrace Violet+ cells). (E) Frequency of CD11b-/Gr-1- undifferentiated murine cells after co-culture. (F) Frequency of SNA+ and Gr-1+ murine cells after co-culture with genetically modified MM1.S cell lines (Cr3 and Cr4) with targeted ST6GAL1 knockout by CRISPR/Cas9. Data are from a single experiment representative of three individual experiments, with n = 4 technical replicates per condition *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by student’s T-test.