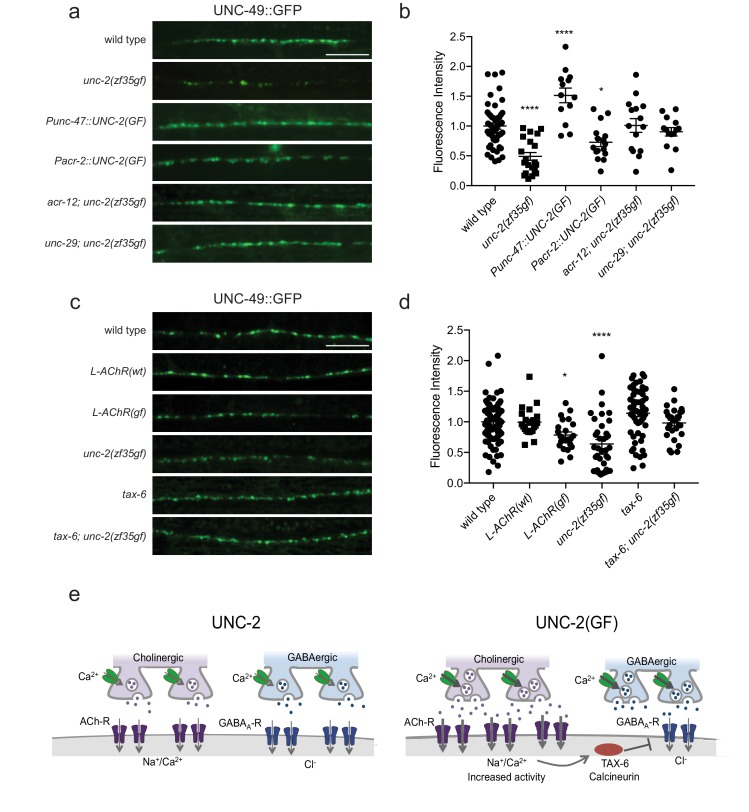
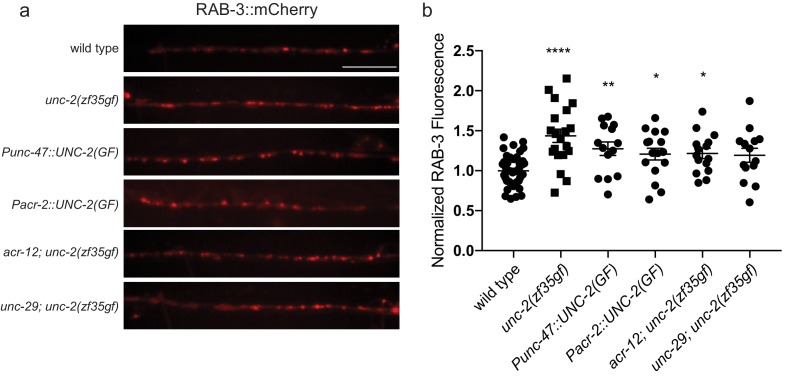
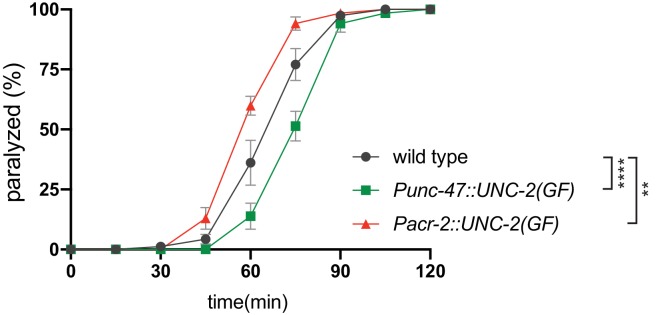
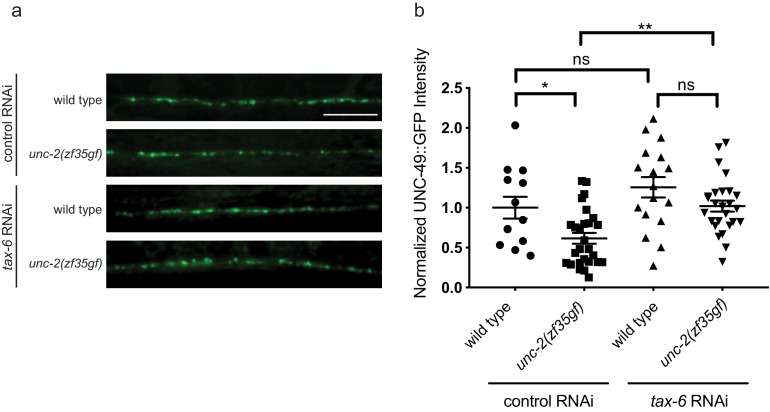
Figure 7. The reduction of GABAA receptor in unc-2(zf35gf) mutants is dependent on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor mediated signaling.
(a and c) Representative images of GABAergic post-synaptic sites labeled with UNC-49::GFP of indicated genotypes. Scale bar represents 10 μm (b) Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of UNC-49::GFP along the nerve cord. Arbitrary fluorescence units of individual animals are normalized to the mean value of wild type. Normalized UNC-49::GFP fluorescence: wild type (1 ± 0.06, n = 41), unc-2(zf35gf) (0.4 ± 0.07, n = 15), Punc-47::UNC-2(GF) (1.5 ± 0.12, n = 13), Pacr-2::UNC-2(GF) (0.7 ± 0.07, n = 16), acr-12; unc-2(zf35gf) (1 ± 0.11, n = 15) and unc-29; unc-2(zf35gf) (0.9 ± 0.07, n = 14). (d) Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of UNC-49::GFP along the nerve cord of indicated genotypes. Arbitrary fluorescence units of individual animals are normalized to the mean value of wild type. Normalized UNC-49::GFP fluorescence: wild type (1 ± 0.04, n = 82), L-AChR(WT) (1 ± 0.05, n = 22), L-AChR(GF) (0.8 ± 0.05, n = 23), unc-2(zf35gf) (0.6 ± 0.07, n = 36), tax-6 (1.1 ± 0.06, n = 54), tax-6; unc-2(zf35gf) (1 ± 0.05, n = 29). For all the quantification above, error bars depict SEM. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. (e) Model: The UNC-2 gain-of-function mutation shifts the E/I balance to an excitation-dominant transmission through the destabilaztion of GABA synapses in a TAX-6/calcineurin-dependent manner (See text for explanation).