Fig. 2. CRISPR/HDR engineering of hybridoma MIH5 to obtain panel of isotype variants.
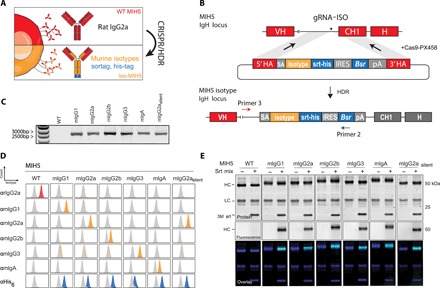
(A) CRISPR/HDR strategy to engineer rIgG2a hybridomas and obtain recombinant hybridomas secreting murine isotypes. (B) The targeted IgH locus of MIH5 with the variable region (VH), constant region 1 (CH1), and hinge annotated. Cas9 is guided by gRNA-ISO to the intronic region upstream of the CH1 is shown. The resulting double-stranded break is subsequently resolved via HDR through a donor construct, leading to an in-frame insertion of an splice acceptor (SA, gray), isotype of choice (yellow), a sortag and his-tag motif (srt-his, blue), an IRES, blasticidin-resistance gene (Bsr), and polyA transcription termination signal (pA) upstream of the native CH1. The insert is enclosed by homology arms (5′ HA and 3′ HA). (C) Three days after electroporation, DNA from CRISPR/HDR-targeted MIH5 populations is obtained for PCR with primer 3 and primer 2 (B). Agarose gel of the PCR product reveals amplicons of the correct size exclusively for the CRISPR/HDR-targeted populations. (D) After selecting monoclonal hybridoma for each isotype, the supernatant of each isotype modified clone was incubated with PD-L1–expressing target cells (CT26). Displayed plots demonstrate that supernatants exclusively contain the engineered isotype variant with a C-terminal his-tag, while the original rIgG2a mAbs is absent. (E) Purified MIH5 isotype variants were effectively labeled with the fluorescent probe GGGCK(FAM) using sortase-mediated ligation.
