Figure 2. Adjusted Cumulative Medication Exposures in Infants with Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Across United States Children’s Hospitals, Restricted Analysis.
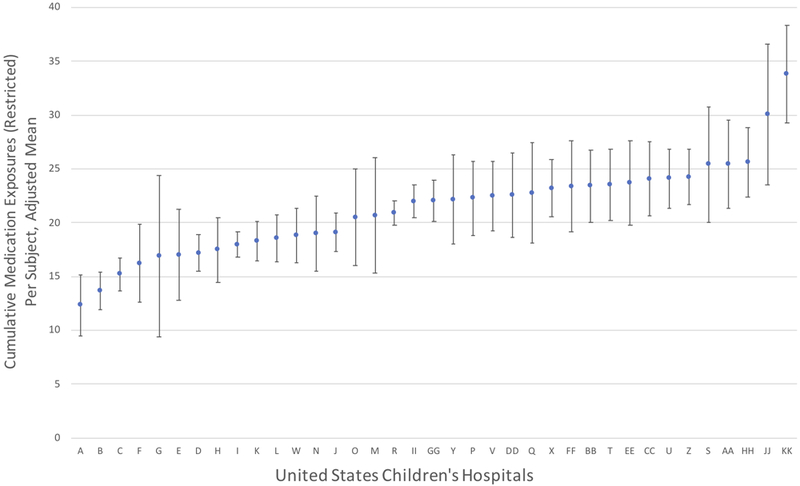
Plot depicts estimated marginal means and 95% confidence intervals for each hospital, ordered from lowest (A) to highest (KK) adjusted mean cumulative medication exposures during the study period (from 36 weeks postmenstrual age to the first of either hospital discharge or one year of age). Medications associated with routine health care maintenance and fluid, electrolyte and nutrition management were restricted from this analysis. Hospital labels (A, B, etc.) correspond to ordering from unrestricted analysis (Figure 1) for consistency and comparison. Variation analysis was restricted to the 37 hospitals with >15 observations. Estimated marginal means were obtained following adjustment for the following infant characteristics in multivariable linear regression analysis: gestational age in completed weeks, sex, maternal race, type of respiratory support at 36 weeks PMA, infection during the hospitalization and the presence of operating room charges during the hospitalization. P < 0.0001 for Wald global test of difference among centers.
