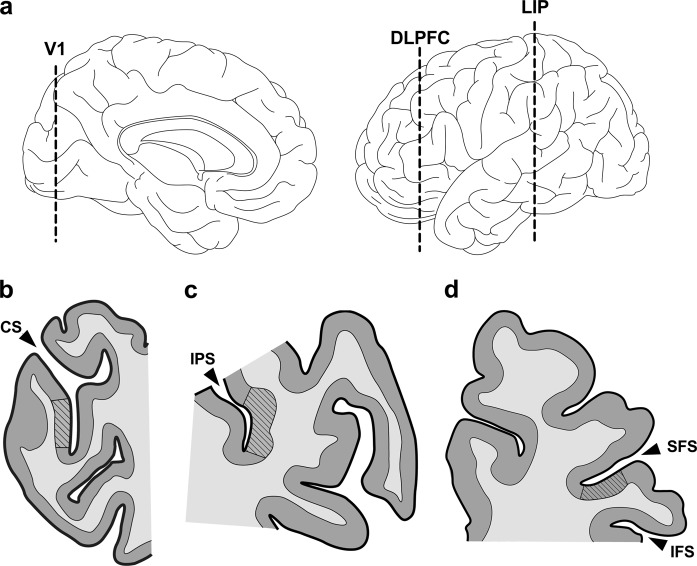
Fig. 1.
Components of the visuospatial working memory pathway represent the rostro–caudal cortical axis. a Rostro–caudal position of human V1, DLPFC, and LIP in medial (left) and lateral (right) view. b–d Representative tissue sections containing V1 (b), LIP (c), and DLPFC (d). For the present study, coronal blocks containing the calcarine sulcus (CS), intraparietal sulcus (IPS), or middle frontal gyrus (bordered by the superior/inferior frontal sulci [SFS/IFS]) were sliced to derive tissue sections containing V1 (BA17), LIP (BA7), and DLPFC (BA46), respectively. Regions of interest (striped areas) were defined by cytoarchitectonic criteria (see text)