Figure 1.
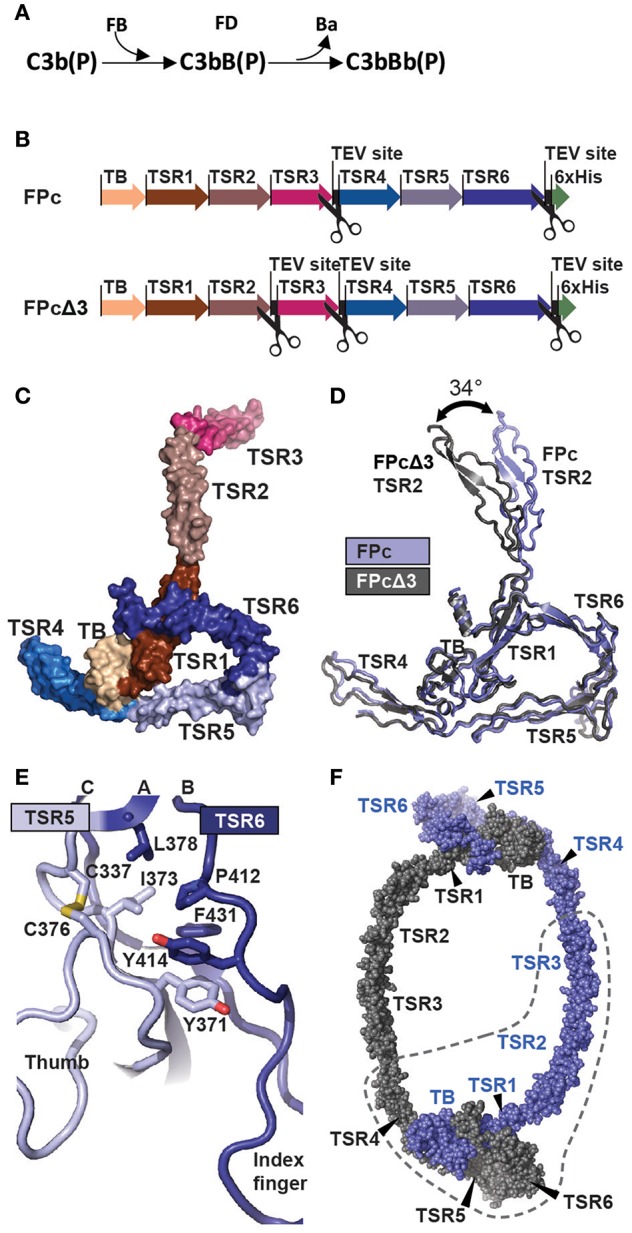
The function and structure of FP. (A) In the complement alternative pathway FP bound C3b can bind FB forming the C3bB(P) AP C3 proconvertases. The serine protease FD can then cleave zymogen FB resulting in the AP C3 convertase C3bBb(P). According to nomenclature, the letter “F” is skipped in complexes of complement proteins. (B) Cartoon of the FPc and FPcΔ3 constructs. The domains are indicated by a thick arrow in the color corresponding to the specific domain. (C) A surface representation of the FPc crystal structure with TB domain and TSR coloring as in panel B. (D) Overlay of the structures of FPc (blue) and FPcΔ3 (gray) shown in a cartoon representation demonstrating the flexibility of the TSR2 domain. (E) A cartoon representation of the interface in FP between TSR5 (light blue) and TSR6 (navy blue). Residues important for the interface are shown as sticks. (F) Theoretical model of a FP dimer with the monomers colored gray and blue, respectively. The dashed line outlines one FPc molecule for comparison with panel C.
