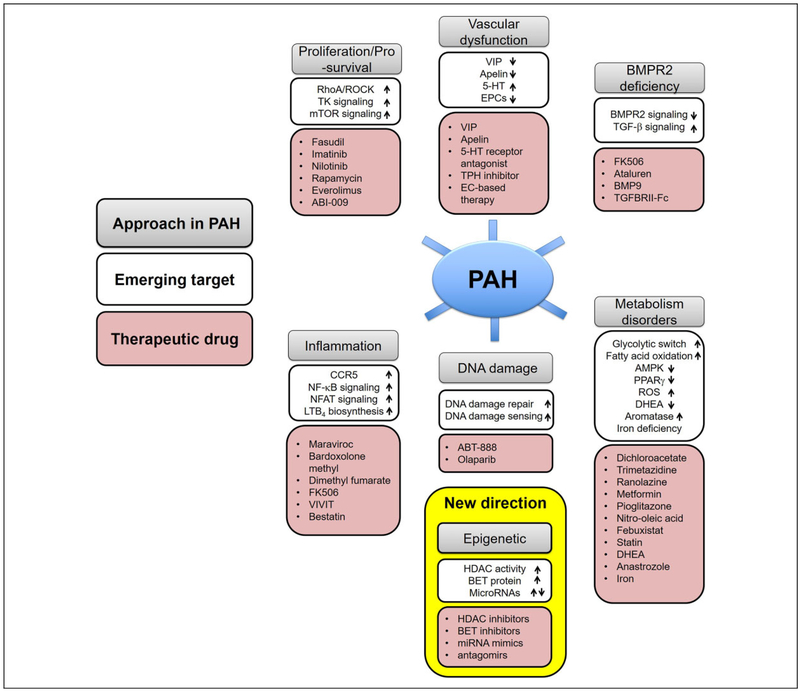
Figure 3.
Emerging therapeutic targets in PAH. An improved understanding of the molecular and genetic mechanisms leading to PAH have provided translational opportunities for the development and testing of novel therapeutics agents. A number of emerging pathways amenable to therapeutic manipulation are summarized. 5-HT indicates serotonin; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BET, bromodomain and extra terminal domain; BMP9, bone morphogenetic protein 9; BMPR2, bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2; CCR5, C-C chemokine receptor 5; DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; EC, endothelial cell; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; HDAC, histone deacetylases; LTB4, leukotriene B4; miRNA, microRNA; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TK, tyrosine kinase; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide.