Figure 4.
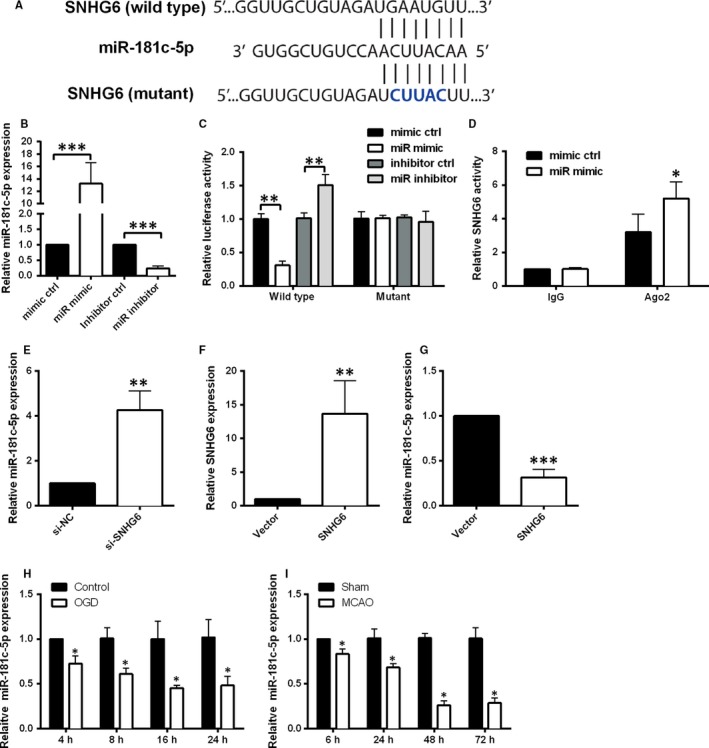
SNHG6 binds directly to miR‐181c‐5p and negatively regulates the expression of miR‐181c‐5p. A, The putative miR‐181c‐5p binding sites of the wild‐type and mutant sequence of SNHG6. B, qRT‐PCR analysis for expression of miR‐181c‐5p in cortical neurons transfected with miR‐181c‐5p mimic, mimic control, miR‐181c‐5p inhibitor or inhibitor control (N = 3). C, Luciferase activity was detected in cortical neurons co‐transfected with miR‐181c‐5p mimic (or mimic control) and reporter vector containing SNHG6 WT (or SNHG6‐MUT) (N = 3). D, RIP analysis for the interaction between SNHG6 and miR‐181c‐5p in cortical neurons with miR‐181c‐5p mimic or mimic control transfection. E, qRT‐PCR analysis for the expression of miR‐181c‐5p in cortical neurons transfected with si‐SNHG6 or si‐NC (N = 3). F, qRT‐PCR analysis for the expression of SNHG6 in cortical neurons transfected with pcDNA3.1 (Vector group) or pcDNA3.1‐SNHG6 (SNHG6 group). G, qRT‐PCR analysis for the expression of miR‐181c‐5p in cortical neurons transfected with pcDNA3.1 (Vector group) or pcDNA3.1‐SNHG6 (SNHG6 group). H, qRT‐PCR analysis for expression of miR‐181c‐5p in cortical neurons at 4, 8, 16 and 24 h after OGD treatment (N = 3). I, qRT‐PCR for expression of miR‐181c‐5p in ischaemic brain tissues at 6, 24, 48 and 72 h after MCAO (N = 6). Data were shown as mean ± SD *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001
