Figure 1.
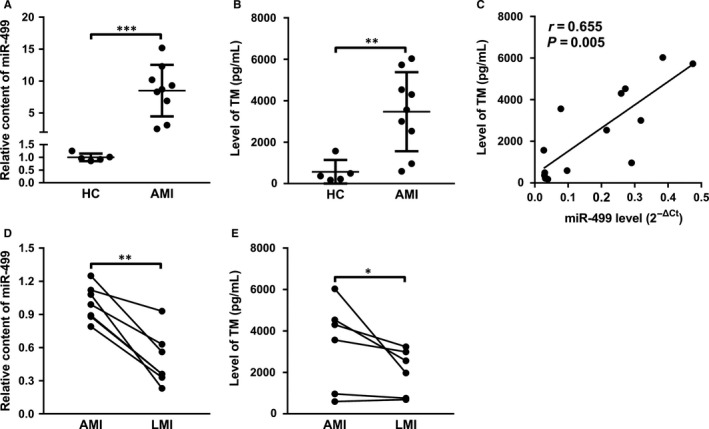
Increased levels of plasma miR‐499 after AMI are directly correlated with endothelial damage. A, Plasma miR‐499 is ~7‐fold higher in patients with AMI (n = 9) than HC (n = 5) (P < 0.001). B, Plasma TM is significantly higher in AMI (n = 9) than HC (n = 5) (P < 0.01). C, Plasma miR‐499 was positively correlated with the TM in the patients with or without AMI (r = 0.655, P = 0.005). D, Plasma miR‐499 is significantly higher in AMI than LMI (n = 6 in each and P < 0.01). E, Plasma TM is significantly higher in AMI than LMI (n = 6 in each and P < 0.05). The levels of miR‐499 were normalized to that of U6 RNA. Data are presented as ‘Mean ± SD’. Mann‐Whitney U test (A, B), Spearman correlation test (C) and Wilcoxon test (D, E) were used for statistical analysis, with * denoting P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001
