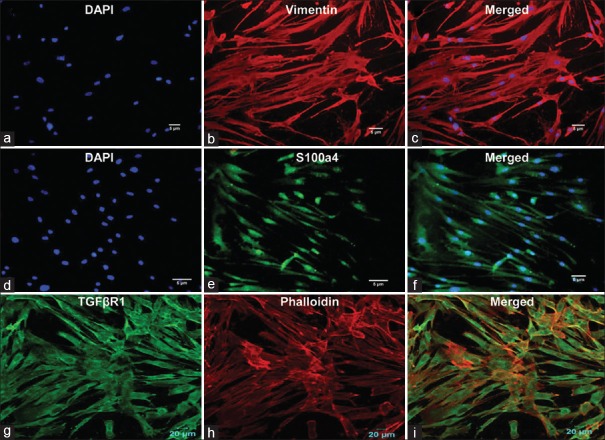
Figure 3.
Immunofluorescence staining of cultured human buccal cells leading to the formation of homogenous fibroblast cells. Vimentin (b and c) staining indicated mesenchymal origin, while s100a4 (e and f) detected the intracellular filaments in fibroblasts. Surface protein receptor (g) transforming growth factor β receptor 1 indicated the fibrotic nature of the differentiated cells, while phalloidin (h) was used to show the presence of actin filaments in such cells. 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining of nucleated cells confirmed the viability of the growing cells (a and d), (i) Merged image (TGFβR1 and phalloidin)