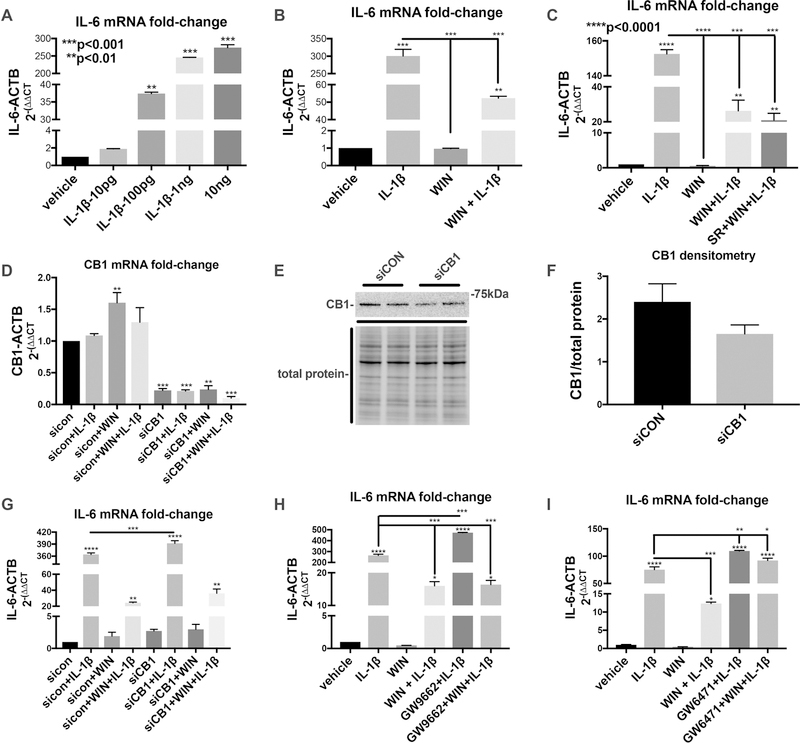
Figure 7. WIN-mediated inhibition of IL-1β-induced inflammatory gene expression is reversed by PPARα antagonist.
(A) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia treated with an increasing dose response of IL-1β. (B) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia treated with vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, and WIN+IL-1β. (C) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia treated with with vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, WIN+IL-1β and SR+WIN+ IL-1β. (D) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia first transfected with control siRNA or CB1-specific siRNA and then vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, and WIN+IL-1β. (E) Immunoblot for CB1 in astroglia first transfected with control siRNA or CB1-specific siRNA. (F) Quantification of CB1 band densitometry normalized to total protein densitometry. (G) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia first transfected with control siRNA or CB1-specific siRNA and then vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, and WIN+IL-1β. (H) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia treated with with vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, WIN+IL-1β and GW9662+WIN+ IL-1β. (I) IL-6 mRNA fold-change after 6 hours in astroglia treated with vehicle, WIN, IL-1β, WIN+IL-1β and GW6471+WIN+ IL-1β. All graphs plot mean ± SEM. All experiments were performed in three independent experiments using at least two astroglial lines with different genetic background. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA.