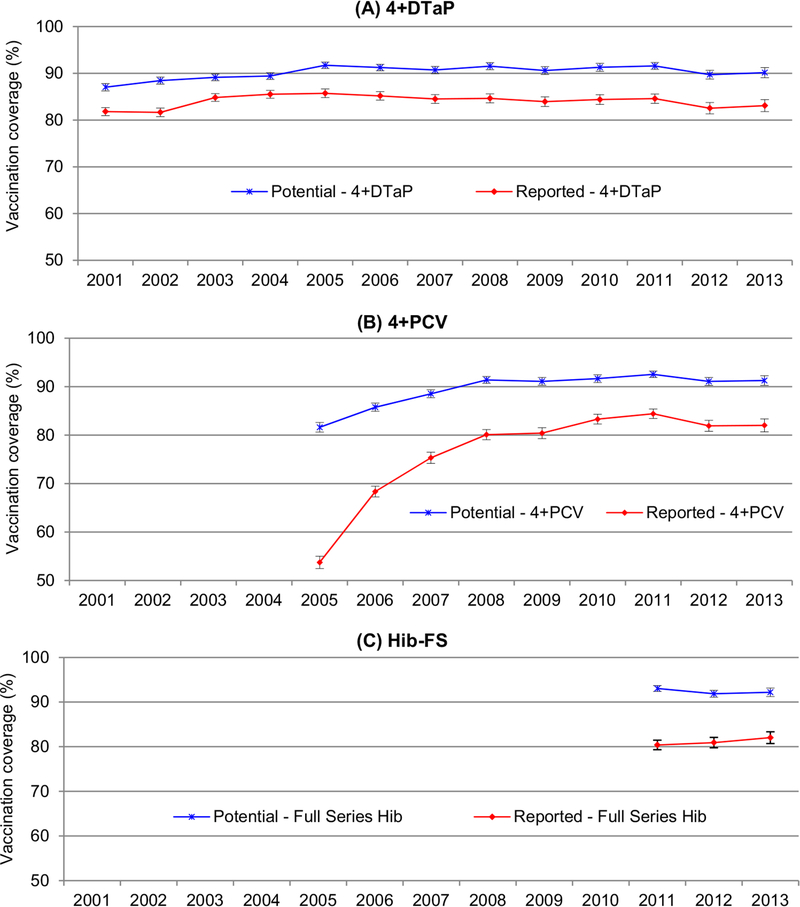
Fig. 1.
Potentially achievable vs. reported vaccination coverage and 95% confidence interval for 4+DTaP*, 4+HPV†, Hib-FS§, National Immunization Survey, United States, 2001–2013. *≥4 doses of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine. † ≥4 doses of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV). § Full series Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine: ≥3 or ≥4 doses of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib-FS) vaccine depending on product type received (includes primary series plus the booster dose). Footnote for (B): Because of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine shortages during 2001–2004 in the United States, children included in the 2001–2004 samples were affected by the deferring of the fourth dose of PCV, therefore the data from NIS 2005–2013 were included for the PCV vaccination study. Footnote for (C): Hib data were limited to 2011–2013 because a shortage of Hib vaccine occurred in the United States during December 2007 to September 2009, children were affected by the temporary recommendation to suspend the booster dose of Hib for Hib-FS vaccine.