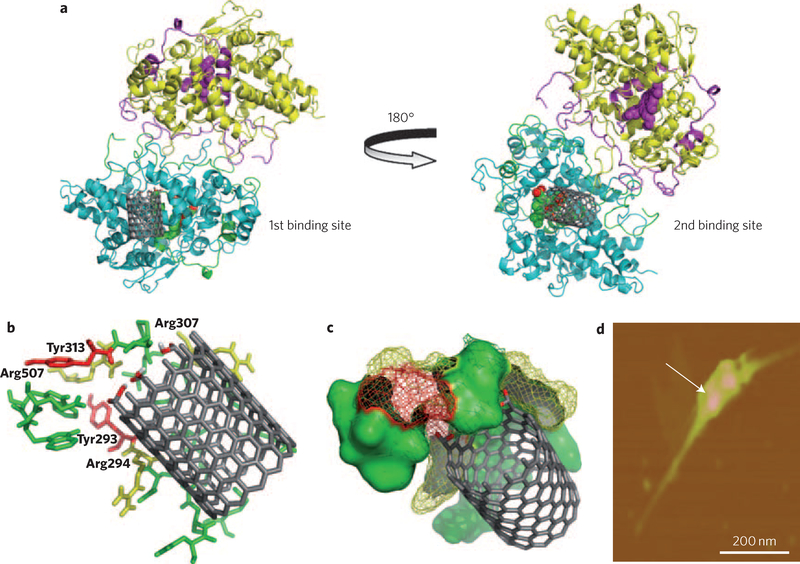
Figure 2 |. Molecular modelling, demonstrating possible nanotube interaction sites on hMPO.
a, Two putative binding sites for nanotubes on the hMPO monomer surface are located on each side of the protein. The best model site with lowest binding energy is shown for carboxylated short-cut nanotubes (left) and pristine nanotubes (right). b, Stabilization of the carboxylated ends of the nanotubes by arginine (yellow) and tyrosine residues (red) in hMPO in the first binding pocket (left). All residues shown are within 5 Å of nanotubes and are predicted to participate in the degradative catalysis of nanotubes. This includes Tyr293, Arg294, Arg307, Tyr313 and Arg507. c, As b, using space-fill representation. d, AFM image confirming the binding of a dimer of hMPO with a single nanotube.